- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Record to Report Process
Record to Report Process
Record to report (R2R) is a finance and accounting management process that involves collecting, processing, analyzing, validating, organizing, and finally reporting accurate financial data. R2R process provides strategic, financial, and operational feedback on the performance of the organization to inform management and external stakeholders. R2R process also covers the steps involved in preparing and reporting on the overall accounts.
Definition of Record to Report Process
This function helps to assist the companies in the preparation and submission of various statutory reports that require in-depth and specialized domain knowledge. This process enables companies to consolidate global performance across various channels and create global income statements and balance sheets. This provides visibility to various channel heads to understand and comment on the key variance drivers with reference to plans and past years' performance. All the activities from recording to reporting of transactions are included in the "Record to Report" process also known as "R2R", “Account to Report”, “A2R”, General Ledger, “Finance & Accounting” process. People with extensive training/experience with knowledge of client/country-specific requirements are important for building an effective “Record to Report” process.
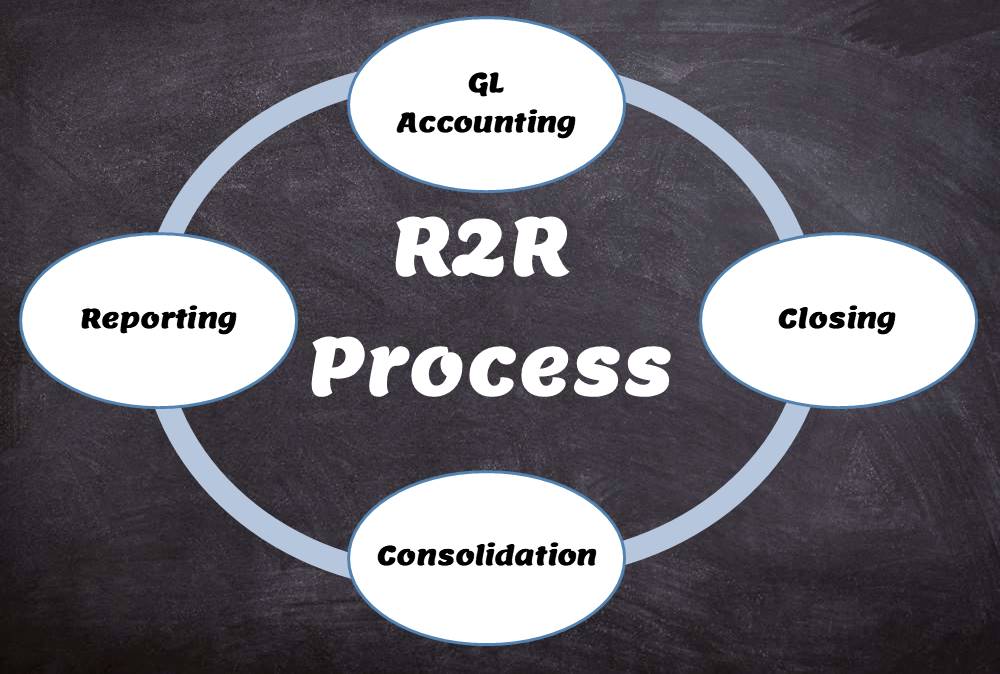
The R2R Process
The record-to-Report process is an end-to-end process that includes, general accounting, sub-ledger accounting, tax compliance, regulatory compliance, financial analysis, and reporting and interacts with the functions of budgeting and forecasting and internal and external audit. It includes all subsequent activities after the recording financial transactions related to the financial close consolidation, through the external reporting of the Company’s financial results. The R2R process ends with the completion of account reconciliations of balances generated during the financial close process.
The four core steps in the record to report process are
- General Ledger Accounting
- Closing of Books
- Consolidation of Accounts
- Reporting of Financials
1. General Ledger Accounting:
The processing cycle is where the majority of data required for the Record to Report process is generated. The R2R process begins when recording occurs in a general ledger singly or jointly on Management GAAP and Statutory accounting basis. This step happens once the maintenance and closure of sub-ledgers are completed. Recording transactions includes documenting revenues (by invoices or sales receipts), and entering purchases (in the account payable account) and expenditures (in the check register). This step sometimes also involves high-level accounting tasks, such as recording sales orders, tracking prospective customers, and projecting sales opportunities and cash flow.
To record and classify a transaction to appropriate accounts, a proper understanding of the accounting equation is and accounting standards and practices is a must. Calculating and summarizing transactions in a traditional accounting system is a tedious process and automated accounting frees accountants from these repetitive tasks by calculating and summarizing hundreds or thousands of individual transactions and generating reports to satisfy a variety of stakeholders.
2. The Closing Cycle:
Once the processing cycle is complete, the next cycle is to close the books. Closing of Management GAAP books is done following the common R2R Organizational Global Closing Calendar along with the closing of statutory accounting books. Close Cycle is the elapsed time for posting transactions to the general ledger and financial reporting systems through locking down the general ledger.
3. The Consolidation Cycle:
The consolidation cycle is the next pivotal step in the Record to Report process and this step allows companies to perform eliminations, reconcile intercompany balances and produce the data required to generate financial statements by entities. The consolidation cycle must address both internal and external reporting needs. Consolidation and elimination include completion of within and outside own Business eliminations, intercompany reconciliations, and other post-close activities leading to final financial statements at the consolidated “Consolidating Entity” segment level.
4. Reporting Cycle:
The reporting cycle is the formal process of data gathering, assimilating, performing analysis, and distributing the results. Throughout a leading practice close and consolidation cycle, management is receiving reports that address key indicators and statistics. The key to this process is the flow of the information necessary to provide accuracy in an efficient manner. This would include information from all source systems and sometimes requires a support process to accomplish it. Reporting cycle includes submission of financial data and commentary to the Organization’s Corporate Headquarters, external reporting, and government reporting.
The accounting system records the economic data about business activities and events, the next logical step is to prepare the business reports and provide them to the stakeholders according to their informational needs. The double-entry system enables accountants to prepare some standard reports like trial balance, profit and loss account, and balance sheet. Accounting reports are based on generally accepted accounting standards and these reports are powerful tools to help the business owner, accountant, banker, or investor analyze the results of their operations. Stakeholders use accounting reports as a primary source of information on which they base their decisions. They use other information as well. For example, in deciding whether to extend credit to a company, a banker might use economic forecasts to assess the future demand for the company’s products. The banker might inquire about the ability and reputation of the managers of the business.
Importance of Record to Report:
The accuracy and integrity of the financial statements largely depend on the efficiency of transactional bookkeeping activities. People with extensive training/experience with knowledge of client/country-specific requirements are important for building an effective “Record to Report” process. This function helps to assist the companies in the preparation and submission of various statutory reports that require in-depth and specialized domain knowledge. This process enables companies to consolidate global performance across various channels and create global income statements and balance sheets. This provides visibility to various channel heads to understand and comment on the key variance drivers with reference to plans and past years' performance.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
-
Period End Accruals, Receipt Accruals, Paid Time-Off Accruals, AP Accruals, Revenue Based Cost Accruals, Perpetual Accruals, Inventory Accruals, Accruals Write Off, PO Receipt Accrual, Cost Accrual, etc. are some of the most complex and generally misconstrued terms in the context of general ledger accounting. In this article, we will explore what is the concept of accrual and how it impacts general ledger accounting.
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved