- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
Legal Forms and Structures
In a rapidly changing national and global business environment, it has become necessary that corporate entities are organized in tune with the emerging economic trends, enable good corporate governance, and enable protection of the interests of the investors and other stakeholders. Further, due to the continuous increase in the complexities of business operation, the forms of corporate organizations are constantly changing.
This section provides an overview of some of the most commonly used legal forms and structures by corporate organizations across the globe along with a brief discussion of related laws, rules, procedures, and regulations that need compliance. How a company structures its long-term operations in a foreign country, effectively defines how it will be taxed hence the choice could have a significant potential effect on the profitability.
Regulations prevalent in most of the countries generally allow foreign entities to choose classification as a corporation (subsidiary), partnership, unincorporated branches; Limited Liability Companies (LLCs), distributor and manufacturer representatives, and joint ventures. Each choice has its own implications and complications. Generally, corporates operate as a separate legal entity with limited liability. Typical business models of foreign corporations conducting business activities in other countries involve wholly-owned Subsidiaries, Joint Ventures, Representative Offices, or Foreign Branches.
What is a Legal Entity?
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. Some of the attributes associated with a legal entity are:
- A legal entity has the legal capacity to enter into agreements or contracts, assume obligations, incur and pay debts, sue and be sued in its own right, and to be held responsible for its actions.
- Legal Entities file the accounts and take care of accounting. Legal Entity is the organizational unit for Financial Accounting for which a completely self-contained set of accounts needs to be drawn up for purposes of external reporting.
- Legal Entity possesses separate existence for tax purposes. Legal Entities pay the taxes and therefore need tax registrations.
- Trade between Legal Entities needs intercompany supported by adequate legal documentation.
- Legal Entities own the money and bank accounts
- Legal Entities comply with whatever needs compliance – The “Legal” in the word “Legal Entity”. This includes recording of all relevant transactions and generating all supporting documents required for financial statements.
- Foreign Branches of such corporations can also assume obligations and have legal obligations to submit financial information to foreign governments.
- Legal entities such as parent companies own or control subsidiaries. A large corporation can own many legal entities as its subsidiaries.
Subsidiaries as Legal Entities:
Subsidiaries are a common feature of business life, and all multinational corporations organize their operations in this way. Examples include holding companies such as Berkshire Hathaway, Time Warner, or Citigroup; as well as more focused companies such as IBM or Xerox. These, and other MNCs, organize their businesses into national and functional subsidiaries, often with multiple levels of subsidiaries.
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation. The controlling entity is called its parent company, parent, or holding company.
A subsidiary may itself have subsidiaries, and these, in turn, may have subsidiaries of their own. A parent and all its subsidiaries together are called a "group", although this term can also apply to cooperate companies and their subsidiaries with varying degrees of shared ownership.
Subsidiaries are separate, distinct legal entities for the purposes of taxation, regulation, and liability. For this reason, they differ from divisions, which are businesses fully integrated within the main company, and not legally or otherwise distinct from it.
For the purposes of liability, taxation, and regulation, subsidiaries are distinct legal entities. A subsidiary can sue and be sued separately from its parent and its obligations will not normally be the obligations of its parent. If a parent company owns a foreign subsidiary, the company under which the subsidiary is incorporated must follow the laws of the country where the subsidiary operates, and the parent company still carries the foreign subsidiary's financials on its books (consolidated financial statements).
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
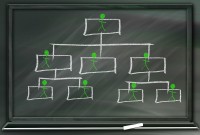
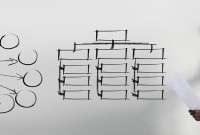
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
-
Business Metrics for Management Reporting
Business metric is a quantifiable measure of an organization's behavior, activities, and performance used to access the status of the targeted business process. Traditionally many metrics were finance based, inwardly focusing on the performance of the organization. Businesses can use various metrics available to monitor, evaluate, and improve their performance across any of the focus areas like sales, sourcing, IT or operations.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
In every journal entry that is recorded, the debits and credits must be equal to ensure that the accounting equation is matched. In this article, we will focus on how to analyze and recorded transactional accounting information by applying the rule of credit and debit. We will also focus on some efficient methods of recording and analyzing transactions.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved