- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- What is a General Ledger?
What is a General Ledger?
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
Difference between Transactions & Financial Transactions:
As discussed earlier, the business enters into many activities and transactions throughout the day. It is not necessary that all activities have a financial impact. For example, if a company issues a Purchase Order for buying certain goods, but no financial transaction has happened unless the goods are delivered and the invoice is raised on the company issuing the purchase order by the supplier. All transactions that have a financial impact only need to be journalized. Transactions having a financial impact are only posted to General Ledger.
What is General Ledger?
Once we have journalized transactions into a general or special journal which are also referred to as "the book of original entry, the transactions need to be entered in the general ledger which is also called "the book of final entry." The general journal and the general ledger both record transactions, but it is the general ledger that groups similar transactions into accounts, and converts the accounting data into meaningful information useful for the stakeholders.
Transactions are first recorded in the general journal and then transferred, or posted, to the ledger, which stores all the charts of accounts of a business. An account is defined as an accounting record that reflects the increases and decreases in a single asset, liability, or owner's equity item (The Accounting Equation!!). In addition, the ledger shows the balance of each account that helps the user understand the final effects of the transactions.
While journals present a chronological listing of a company's daily transactions, ledgers are organized by account. As a result, financial statements such as Balance Sheets and Income Statements can only be generated from the general ledger not directly from the journals.
Accounts in a ledger are simply groupings of interest. Sub Accounts are created for five types of accounts Assets, Liabilities, Equities, Revenues, or Expenses. Separate records are created to classify these accounts further to help to understand the accounting data at a granular level. Based on the individual business needs the number and variety of sub-accounts (natural accounts) in a given business can vary significantly. In order to group account information more usefully, a company may use subsidiary ledgers as well as a general ledger.
Format of General Ledger:
The purpose of the general ledger is to categorize the information into accounts and provide the users with different account balances. This categorization ensures that the data is organized and easily accessible to convert them into trial balance and finally convert it to financial statements. As the rules of debit and credit and the accounting equation still apply, the summation of the balances of all the accounts in a General Ledger is always equal to zero, because for every debit in Journal we have also created a corresponding credit. The standard format helps organize financial information in one place.
Standard general ledger format generally contains the following information:
- The chart of accounts- classified into five account types - Assets, Liabilities, Equities, Revenues, or Expenses.
- The account's title is the name of the account and must exactly match the account name as defined in the master chart of accounts by the organization.
- The Date columns – A general ledger may capture several dates, like the entered date, transaction date, accounting date, and the posting date. These dates may be the same or may vary based on the business internal policies.
- The Particulars column explaining the nature and purpose of the transactions that are being captured against the respective accounts and amounts.
- The Post Reference (P.R.) column specifying the reference information to the posting event, tying the transaction back to the originating journal.
- The Debit column representing the amount of debit posted to the account.
- The Credit column representing the amount of credit posted to the account.
- The Debit Credit Balance (DR./CR.) column to indicate the sign of the final balance. Sometimes a negative (-) is used to represent credit balances.
- The Balance column which keeps a running balance of each account. Due to this balance column, the ledger is referred to as a "balanced column account."
A good general ledger software application will provide management with accurate, up-to-date information in order to make short and long term business decisions. It also has inbuilt controls and processes necessary, to ensure that the correct information is reported. Income statements, balance sheets, and statements of cash flow are standard reports needed by management to judge business progress and these reports can be built using the trial balance created in General Ledger.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
Understand what we mean by GAAP to STAT adjustments. This article discusses the different standards that are used for multiple representations of the financial results for global organizations. Understand the meaning of US GAAP, Local GAAP, STAT, IFRS, and STAT. Finally, understand why accounting differences arise and how they are adjusted for different financial representations.
-
Accrued expenses, sometimes referred to as accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts. Discuss the need to record accrued liabilities and why they require an adjustment entry. Understand the treatment for these entries once the accounting period is closed and learn to differentiate when the commitments become liabilities.
-
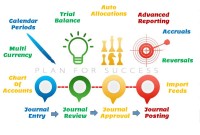
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
Reversing Journals are special journals that are automatically reversed after a specified date. A reversing entry is a journal entry to “undo” an adjusting entry. When you create a reversing journal entry it nullifies the accounting impact of the original entry. Reversing entries make it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the need for certain compound entries. See an example of reversing journal entry!
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved