- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Leadership Theories
- Trait Theory of Leadership
Trait Theory of Leadership
Trait Theory of Leadership is based on the assumption that people are born with inherited traits and some traits are particularly suited to leadership. The theory aims to discover specific leadership & personality traits and characteristics proven to predict the likelihood of success or failure of a leader.
What are Personality Traits?
The trait approach to personality is one of the major theoretical areas in the study of human personality and is focused on differences between individuals. The trait approach was one of the first systematic attempts to study leadership. The combination and interaction of various traits forms a personality that is unique to each individual. Trait theory is focused on identifying and measuring these individual personality characteristics known as Traits.
Traits: Also called dispositions, Traits can be defined as habitual patterns of behavior, thought, and emotion. Traits are relatively stable over time, differ across individuals and influence behavior. Traits are external behaviors that emerge from internal beliefs and processes.
What is Trait Theory of Leadership?
Trait Theory of Leadership is based on the assumption that people are born with inherited traits and some traits are particularly suited to leadership. People who make effective leaders have the right (or sufficient) combination of traits and great leaders has some common personality characteristics. Trait theories help us identify traits and dispositions that are helpful when leading others. This theory as described by Kelly (1974) attempts to classify what personal characteristics such as physical, personality and mental, are associated with leadership success. Trait theory relies on research that relates various traits to the success of a leader.
Quotes on Traits:
“Leadership consists not in degrees of technique but in traits of character; it requires moral rather than athletic or intellectual effort, and it imposes on both leader and follower alike the burdens of self-restraint.” - Lewis H. Lapham
“The screenwriters I know share a few personality traits and one of them is anxiety.” - Tony Gilroy
“I think in the end, when you're famous, people like to narrow you down to a few personality traits. I think I've just become this ambitious, say-whatever's-on-her-mind, intimidating person. And that's part of my personality, but it's certainly not anywhere near the whole thing.” - Madonna Ciccone
“The moment a person forms a theory, his imagination sees in every object only the traits which favor that theory” - Thomas Jefferson
Overview of Trait Theory of Leadership:
Early research on leadership was based on the psychological focus of the day, which was of people having inherited characteristics or traits. The trait theory of leadership focused on analyzing mental, physical and social characteristic in order to gain more understanding of what is the characteristic or the combination of characteristics that are common among leaders. There have been many different studies of leadership traits and attention was put on discovering these traits, often by studying successful leaders, but with the underlying assumption that if other people could also be found with these traits, then they, too, could also become great leaders.
Advantages of Trait Theory of Leadership:
The trait theory is naturally pleasing theory and gives constructive information about leadership. Lot of research has validated the foundation and basis of the theory and it can be applied by people at all levels in all types of organizations. Managers can utilize the information from the theory to evaluate their position in the organization and to assess how their position can be made stronger in the organization. It serves as a yardstick against which the leadership traits of an individual can be assessed and individuals can get an in-depth understanding of their identity and the way they will affect others in the organization. This theory makes the manager aware of their strengths and weaknesses and thus they get an understanding of how they can develop their leadership qualities. It gives a detailed knowledge and understanding of the leader element in the leadership process.
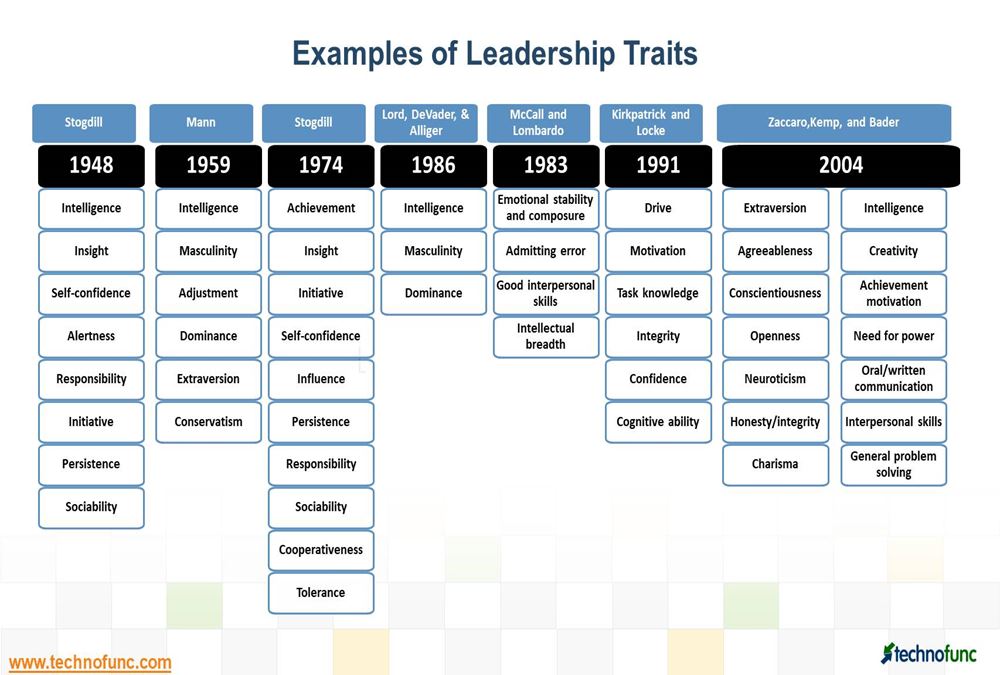
Examples of Leadership Traits:
A lengthy list of traits has been made to describe an effective leader in terms of certain characteristics. Given below is outcome of studies on leadership traits and characteristics with reference to timelines in terms of years:
Criticism / Arguments against - The Trait Theory of Leadership:
Many arguments are made against the leadership theory of traits and it has some inherent limitations as during the 1930s the field of Psychometrics was in its early years. The greatest argument is that if particular traits are key differentiator of leadership, then how do we explain people who possess these qualities but are not leaders? This question is one of the difficulties in using trait theories to explain leadership.
These characteristics according to some people are considered valid indicators of successful leaders, but if you compare leaders by various physical personality and intelligence traits, you may find very little agreement on these. Some findings point out to the fact that leaders are intelligent individuals. But they do not provide any clue as to whether leaders are brighter than their followers or are as close to them in intelligence.
This theory is quite complex and there is bound to be some subjective judgment in determining who is regarded as a ‘good’ or ‘successful’ leader and many of these factors are situational related factors. The followers have a significant effect on the job accomplished by the leader. Trait theory completely ignores the followers and the situations that also help a leader to be successful. To be more objective, traits of the person as well as demand of the situation together determine the effectiveness of the leader.
Some of the personality traits are overlapping with each other. Therefore, you need to be cautious in stating, personality or any other characteristic as a cause of successful leadership. You must ask the questions: Who is a successful leader? Is he far superior physically? Is he far brighter? Is he more mature as a person? Is he more motivated to achieve his goal? Does he have more consideration for his followers? Etc.
Moreover the list of possible traits tends to be very long and personality traits measurement weren't reliable across studies. More than 100 different traits of successful leaders in various leadership positions have been identified. These descriptions are simply generalities and there exists disagreement over which traits are the most important for an effective leader. This theory does not offer explanations between the relation of each characteristic and its impact on leadership. Some of the traits may describe a successful leader but predicting successful leaders on the basis of traits alone is not a correct approach.
Stogdill in 1948, suggested that no consistent set of traits differentiated leaders from non-leaders across a variety of situations implying that an individual with certain traits who has been successful in one situation might not be as effective in another situation and this led to researchers concluding that traits were to be considered as relative to the requirements of the situation.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Certain generally accepted truths or principles of communication are important to consider when communicating with others. These principles hold true for all people in every culture. By understanding these principles, you will experience greater communication effectiveness. An effective communication system is one that achieved its objectives. Communication is effective where there are no barriers to communication.
-
Idiosyncrasy Credit Model of Leadership builds upon the awareness that when the emergent leader meets the team's expectations, idiosyncrasy credits are awarded. These credits depend on how the leader fulfilled follower's expectations and what is the impact of the leader's decisions on the follower. When the balance of credits shifts, another leader will emerge.
-
Theory Z also called the "Japanese Management" style is a leadership theory of human motivation focused on organizational behavior, communication, and development. It assumes that employees want to enter into long term partnerships with their employers and peers. Offering stable jobs with an associated focus on the well-being of employees results in increased employee loyalty to the company.
-
According to the three-skill approach of Katz, the individual's leadership abilities vary depending on where leaders are in a management hierarchy. The practical implication of skills approach to leadership is that leaders can improve their capabilities in leadership skills through training and experience.
-
The Path-Goal theory defines the characteristics of followers and organizational context and the corresponding leadership style best suited to these factors. A leader should adapt to a behavior that is most relevant for a given employee and work environment mix to achieve a goal. The application of theory drives increased employees' motivation, empowerment, and satisfaction resulting in increased productivity.
-
The ten most important qualities that define a good leader are self-awareness, interpersonal and communication skills, ethical values, organizational consciousness, self-confidence, adaptability and flexibility, imagination and creativity, focus & result-orientation, continuous self-development and accountability and ownership for his actions. These ten qualities of leadership every good leader should possess to a certain extent and must continually strive to develop them.
-
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy (SFP) Leader Theory
Pygmalion theory of Leadership is a model of SFP at work involving supervisory expectancy based on the pygmalion effect. This effect is a type of self-fulfilling prophecy (SFP) in which raising leader's expectations regarding subordinate performance boosts the group's performance. Managers who are led to demand more from their team, lead the team to better performance. There is some evidence that the SFP effect does exists.
-
Self-leadership is a normative model of self-influence by the use of several behavioral strategies to gain a comprehensive self-influence perspective about oneself. Self-leadership is developing an understanding of your capabilities and abilities to influence your own communication, emotions, and behaviors to lead and influence others. Self-leadership is about personal growth and developing foresight.
-
Investment Theory of Creativity
Sternberg in the year 2006, proposed the investment and confluence theory focused on understanding creativity. According to the investment theory, creativity requires a confluence of six distinct but interrelated resources known as intellectual abilities, knowledge, styles of thinking, personality, motivation, and environment. It emphasizes that creativity is not about one thing, but about a system of things.
-
The Hersey and Blanchard Situational Theory model suggests that a leader must adapt his leadership style based on task and relationship behaviors appropriate to the situation. Leadership style is dependent on the maturity level and abilities of followers. Under this model, successful leadership is both task-relevant and relationship-relevant.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










