- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Using Adjustment Period
GL - Using Adjustment Period
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
What is the Adjustment Period?
Any accounting period created specifically for entering adjustment and closing entries is known as adjustment period. The dates in the adjustment period overlap with the normal accounting periods in automated systems. Organizations create one accounting period as "Year Open Period” which is the first period in the accounting calendar to clear “carried over balances” from last financial year. Similarly accountants may define the last period of the accounting calendar as "Year Close Period" where adjustment transactions and closing entries are posted for the current accounting calendar. These periods are generally known as “Adjustment Periods”, sometimes are also referred to as “Zero Periods”. Most ERP’s and automated general ledger systems provide the functionality to define adjustment periods.
Benefits of Adjustment Periods:
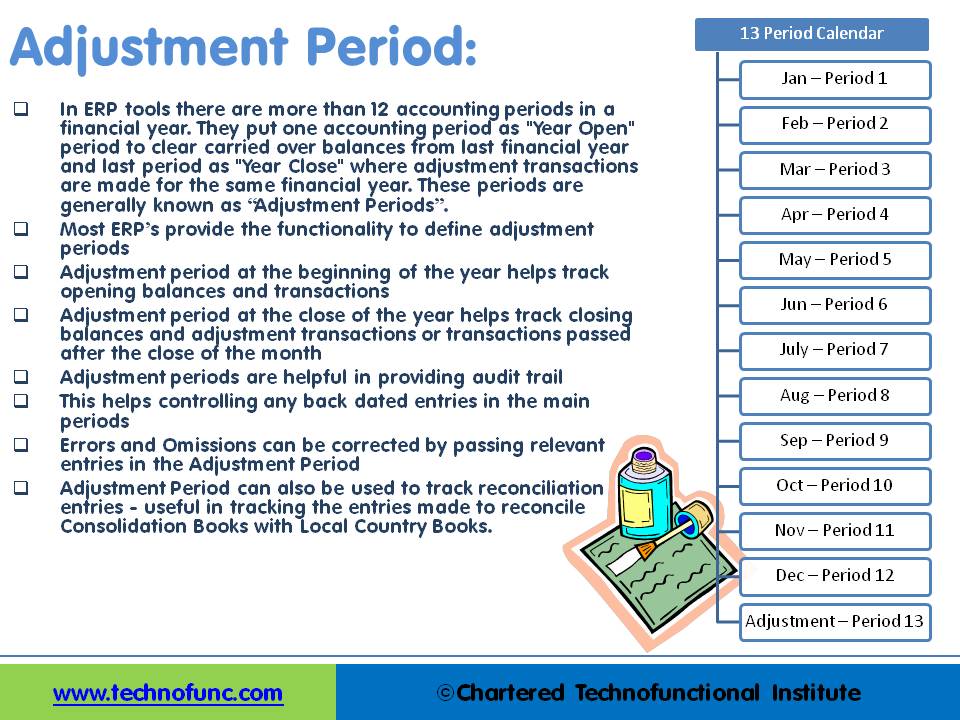
Opening Adjustment Period: Adjustment period at the beginning of the year helps tracks opening balances and transactions. At the beginning of the year user can create journals to transfer their opening balances for the current accounting year. Generally there is an time overlap between the opening of the new financial year and finalization of audit of the previous year. This results in creation of many adjustment entries in the previous year that has an impact on the opening balances of the current year. Users are able to capture those adjustments in a separate “opening adjustment period” to keep a complete track of their normal and adjustment entries. The starting period “Zero” is used to store the starting balance for each balance sheet account.
Closing Adjustment Period:
Similarly, defining an adjustment period at the close of the year helps track closing balances and adjustment transactions. Multiple closing periods allow generation of financial statements reflecting various stages of closing and are helpful in providing complete audit trail. This also helps controlling any back dated entries in the main accounting periods.
Tracking of Errors & Omissions:
Errors and Omissions discovered after the year close can be corrected by passing relevant entries in the Adjustment Period. This will not impact your reported balances; however will create an audit trail for the transactions that need to be take care of next year.
Stat to Management Reconciliation:
Adjustment Period can also be used to track reconciliation entries. Large corporations need to pass many reconciliation entries to tally their Statutory and Main Consolidation Books. Adjustment period is useful in tracking the entries made to reconcile the consolidation books with the Local Country Books.
Exclusion for Management Reporting:
After the close of the books, a large number of entries like accounting entries for accrual or provisions need to be made in the accounting books to comply with the accounting standards and legal regulations. Management however is generally interested in operational data to do their planning and forecasting activities. By limiting adjustment and statutory entries to adjustment period management reports can be driven from same accounting books by excluding adjustment periods from the reports.
Challenges of using Adjustment Periods:
Adjustment periods have some inherent challenges which have been discussed below:
- Automated Accounting Packages comes with many standard reports. You might need to evaluate the impact of adjustment periods on these reports.
- While reversing journal entries; users need to take precaution to select the period in which they want the reversals to happen. ERPs by default might select the adjustment period.
- You may need to decide whether adjustment period should be included or excluded in your comparative reports.
- Similarly you may need to decide whether adjustment period need to be included in any management reports, especially the ones that can be compared with your statutory published results.
How to track adjustment entries without adjustment period?
Defining adjustment periods is totally optional and decision must be based on company’s requirement on the factors discussed above. Alternate solution to defining adjustment periods could be to define a separate cost center (department, division, profit center etc.). All year-end adjustment entries are made using this cost center and this unit is included for statutory consolidation but excluded for management reporting.
Diagram: Figure given at bottom gives a pictorial representation of a calendar with 13 effective periods having one adjustment period at the year end. While reporting your financial results you need to include your beginning of the year adjustment period with the first calendar period and your last adjustment period with the last reporting period.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
GL - Accrued / Unbilled Revenue
Accrued revenues (also called accrued assets) are revenues already earned but not yet paid by the customer or posted to the general ledger. Understand what we mean by the terms accrued revenue, accrued assets, and unbilled revenue. Explore the business conditions that require recognition of accrued revenue in the books of accounts and some industries where this practice is prevalent.
-
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
-
Legal Structures in Businesses
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
GL - Recurring Journal Entries
A “Recurring Journal” is a journal that needs to be repeated and processed periodically. Recurring Entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly, such as fixed rent or insurance to be paid every month. Learn the various methods that can be used to generate recurring journals. See some examples and explore the generic process to create recurring journals in any automated system.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved