- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- General Ledger Process Flow
General Ledger Process Flow
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
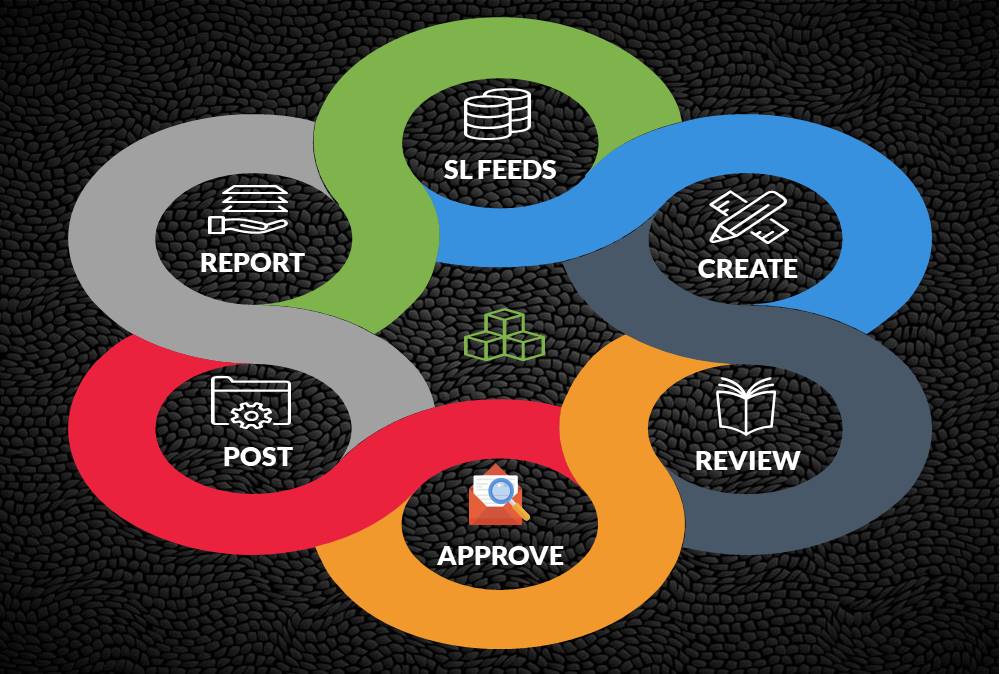
GL process flow is a five-step process from recording the transactions in the system to finally running the reports containing financial data out of the system. The input for GL Process Flow is the raw accounting data and the output is the accounting reports that can be used to provide various levels of financial information.
The steps in the general ledger process flow are:
- Step1. Create Journal or Import Journal from Sub‐Ledger
- Step2: Review Journals
- Step3: Approve Journals
- Step4: Journals Posting
- Step5: Run Financial Reports
Step 1: Create Journal or Import Journal from Sub‐Ledger:
Accounting Journals can be created directly in General Ledger. They can also be created in subsidiary ledgers and can then be imported to General Ledger. In the previous lesson, we saw some examples of commonly used subsidiary ledgers. Companies extensively use modules like accounts receivable, accounts payable, inventory, assets, projects, and cash management subsidiary ledgers. Data created in these sub-systems need to be imported to the general ledger for further processing, The accounting lines from sub-ledgers can be imported in summarized form or detailed form.
General Ledger also allows users to directly add transactions in the GL. In that case, you need to follow the accounting principles and the steps explained in the accounting process. At this stage, the journals are entered into the system and available for further processing, but they have not impacted the general ledger account balances yet.
Step 2: Review Journals:
Once the Journal is available in the General Ledger System you can query the journals that have been created. While reviewing the journal, you can make edits/corrections if required.
You might need to make some adjustments to the journals coming from other sources if you want to change the accounts or amounts that are coming from the sub-systems. Review functionality gives the capability to query the journals based on different parameters and also make edits if required.
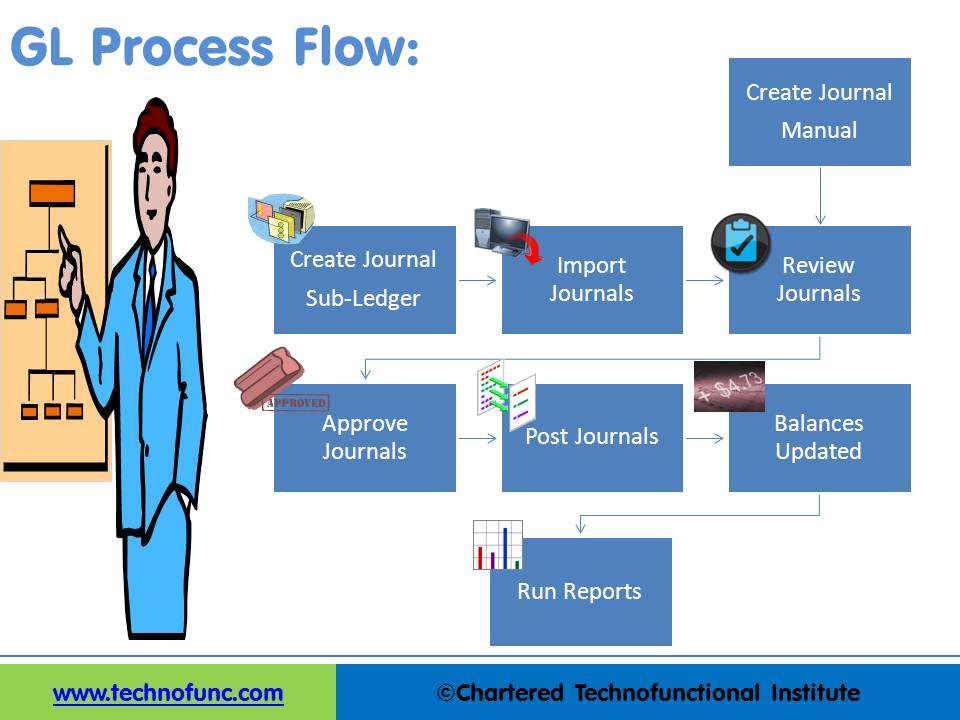
Step 3: Approve Journals:
Accounting prudence requires that all financial transactions should be reviewed by someone other than the person creating the transaction. Approval ensures the validity and correctness of the transaction. The segregation of the Duties concept requires that the responsibility for related operations should be divided among two or more persons. This decreases the possibility of errors and fraud.
In this step, the system will validate the journal batch, determine if approval is required, and submit the batch to approvers (if required), then notifies appropriate individuals of the approval results. Email notifications can be sent to the approvers using the system and they can review and approve the journals. This step is generally optional and many organizations skip this step by putting additional controls in the process. If this feature is enabled then the journal cannot be posted unless it has been approved.
Step 4: Journals Posting:
An important feature of the general ledger is the "Balance" column, which keeps a running balance for each of the accounts pertaining to which transactions are happening. The transactional data captured through journals in the previous steps is transferred periodically to the columns in the general ledger. Journals posting is a process of updating the database with the amounts.
The volume of transactions carried out by a business will indicate how often to post. A busier company may post daily, while other companies may post weekly or monthly. Periodic postings is required to ensure balances for accounts are current, so the business has the up-to-date financial information it needs to make quick decisions. All transactions must be posted to the ledger at the end of an accounting period. Once the Journals are posted users can query for updated account balances using the account inquiry functions.
Journals Balances Updated: The posting process updates the journal balances. You can inquiry about the account balances in General Ledger for all posted transactions.
Step 5: Run Financial Reports:
One way to determine the financial progress of any organization is to look at the profit gained by a business. Once you have the account balances and transactional data available in the system they need to be formatted to meaningful information that can help users understand the financial history as well as equip them to make informed decisions. To enable these business users to need many types of financial reports.
The next step in the general ledger process is to generate these useful reports and the most common reports run from General Ledger are Transactions Register and Trial Balance Report. ERPs come with a large number of seeded reports as well as with tools to define user-specified reports.
Given above is the generic general ledger process. Some systems may have slight variations to the above process, but the underlying concepts remain more or less the same!
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
-
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
-
Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Typically, the accounts of the general ledger are sorted into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses.
-
The sole trader organization (also called proprietorship) is the oldest form of organization and the most common form of organization for small businesses even today. In a proprietorship the enterprise is owned and controlled only by one person. This form is one of the most popular forms because of the advantages it offers. It is the simplest and easiest to form.
-
When the quantum of business is expected to be moderate and the entrepreneur desires that the risk involved in the operation be shared, he or she may prefer a partnership. A partnership comes into existence when two or more persons agree to share the profits of a business, which they run together.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
In every journal entry that is recorded, the debits and credits must be equal to ensure that the accounting equation is matched. In this article, we will focus on how to analyze and recorded transactional accounting information by applying the rule of credit and debit. We will also focus on some efficient methods of recording and analyzing transactions.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved