- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- HRMS & Payroll
- Digital Age and Dynamic Business Environment
Digital Age and Dynamic Business Environment
The digital age, as per yourdictionary.com is also called the information age, is defined as the time period starting in the 1970s with the introduction of the personal computer with subsequent technology introduced providing the ability to transfer information freely and quickly.
The digital age, as per yourdictionary.com is also called the information age, is defined as the time period starting in the 1970s with the introduction of the personal computer with subsequent technology introduced providing the ability to transfer information freely and quickly.
The time period in which we live now where Internet and email are available is an example of the digital age.
The digital age technologies have displaced established technology resulting in a completely new way of doing business and creating opportunities for emergence of a new industry.
These technologies have disrupted the way traditional companies have conducted businesses and both old and new businesses must embrace these disruptive technologies to stay relevant and to meet customer needs.
Here are a few examples of disruptive technologies in 1990’s that transformed established businesses to newer ways of working:
- personal computer replaced typewriter
- Internet enabled Email replaced letter-writing disrupting greeting card industries.
- Cell phones enabled people to call anywhere disrupting telecom industry.
- Laptop and mobile computing made mobile workforce possible.
- Smartphones disrupted pocket cameras, MP3 players, calculators and GPS devices,
- Social networking disrupted telephone, email, instant messaging and event planning.
The last decade has seen an increased intensity in industrial competition, in which cycle times are shrinking and the volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity have opened opportunities and challenges alike
The above listed are just a few examples of disruptions in the 1990’s that have set the stage for continuous evolution in technology to what is observed today. Business services functions – finance, human resources, procurement and IT – are under pressure to adapt the way they deliver services to the demands of the digital age.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
Legal Structures in Businesses
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
GL - Unearned / Deferred Revenue
Unearned revenue is a liability to the entity until the revenue is earned. Learn the concept of unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue. Gain an understanding of business scenarios in which organizations need to park their receipts as unearned. Look at some real-life examples and understand the accounting treatment for unearned revenue. Finally, look at how the concept is treated in the ERPs or automated systems.
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
-
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
-
Understand what we mean by GAAP to STAT adjustments. This article discusses the different standards that are used for multiple representations of the financial results for global organizations. Understand the meaning of US GAAP, Local GAAP, STAT, IFRS, and STAT. Finally, understand why accounting differences arise and how they are adjusted for different financial representations.
-
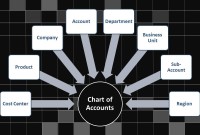
GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA has transitioned from the legacy accounts, capturing just the natural account, to modern-day multidimensional COA structures capturing all accounting dimensions pertaining to underlying data enabling a granular level of reporting. Learn more about the role of COA in modern accounting systems.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved