- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Legal Structures in Businesses
Legal Structures in Businesses
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
Businesses not only vary in size and industry but also in their ownership. Most businesses evolve from being owned by just one person to a small group of people and eventually being managed by a large numbers of shareholders. Different ownership structures overlap with different legal forms that a business can take. A business’s legal and ownership structure determines many of its legal responsibilities.
How a company structures its long term operations in his own country and for expansion to foreign countries, effectively defines how it will be taxed hence the choice could have a significantly potential effect on the profitability. Regulations prevalent in most of the countries generally allow foreign entities to choose classification as a corporation (subsidiary), partnership, unincorporated branches; Limited Liability Companies (LLCs), distributor and manufacturer representatives and joint ventures. Each choice has its own implications and complications. Generally corporates operate as a separate legal entity with limited liability. Typical business models of foreign corporations conducting business activities in other countries involve wholly owned Subsidiaries, Joint Ventures, Representative Offices or Foreign Branches. This section provides an overview of some of the most commonly used legal forms and structures by corporate organizations across globe.
Types of Important Legal Structures:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Company Form of Organization
- Legal Entity
- Corporation or Conglomerate
- Subsidiary - Domestic and Foreign
- Branches - Domestic and Foreign
- Representative Office
- Joint Venture
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
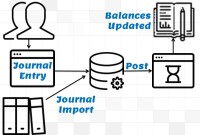
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
For any company that has a large number of transactions, putting all the details in the general ledger is not feasible. Hence it needs to be supported by one or more subsidiary ledgers that provide details for accounts in the general ledger. Understand the concept of the subsidiary ledgers and control accounts.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
Accrued expenses, sometimes referred to as accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts. Discuss the need to record accrued liabilities and why they require an adjustment entry. Understand the treatment for these entries once the accounting period is closed and learn to differentiate when the commitments become liabilities.
-
Prepayments and Prepaid Expenses
Prepayments are the payment of a bill, operating expense, or non-operating expense that settle an account before it becomes due. Learn the concept of prepaid expenses. Understand the accounting treatment for prepaid expenses. Understand the concept by looking at some practical examples and finally learn the adjusting entry for these expenses.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
-
In this article we will help you understand the double-entry accounting system and state the accounting equation and define each element of the equation. Then we will describe and illustrate how business transactions can be recorded in terms of the resulting change in the elements of the accounting equation.
-
GL - Recurring Journal Entries
A “Recurring Journal” is a journal that needs to be repeated and processed periodically. Recurring Entries are business transactions that are repeated regularly, such as fixed rent or insurance to be paid every month. Learn the various methods that can be used to generate recurring journals. See some examples and explore the generic process to create recurring journals in any automated system.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved