- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Intercompany Accounting
GL - Intercompany Accounting
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
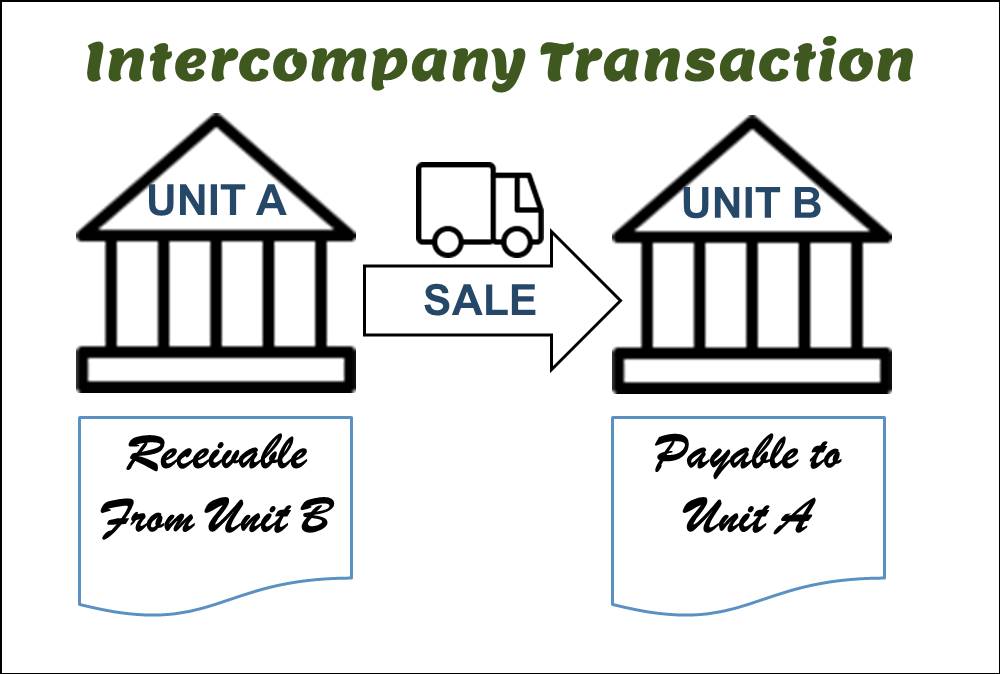
What are intercompany transactions?
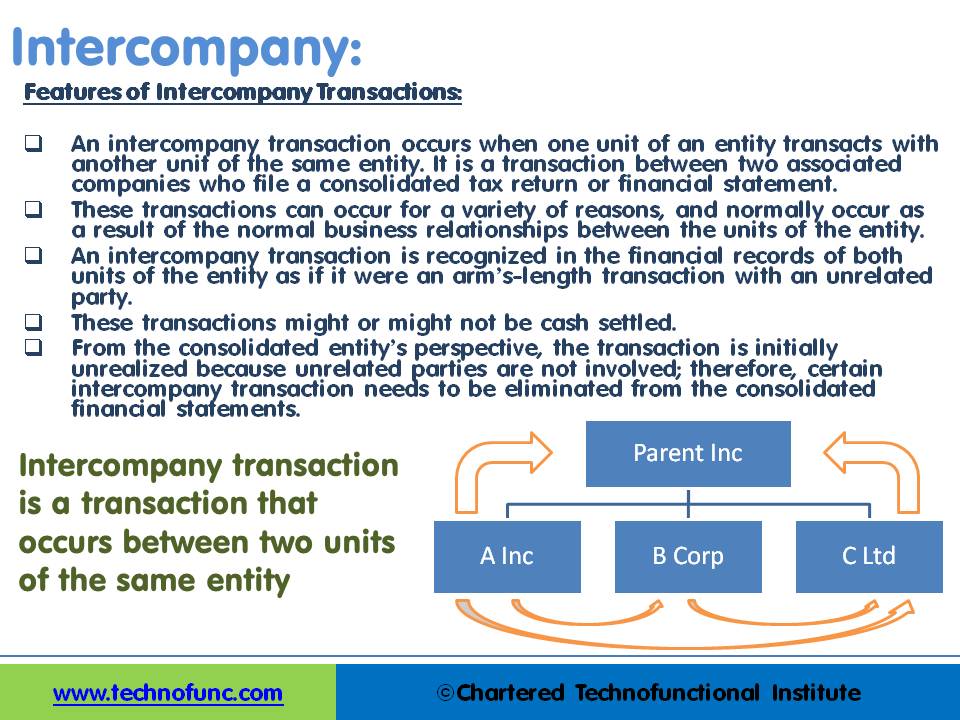
An intercompany transaction occurs when one unit of an entity is involved in a transaction with another unit of the same entity. Most economic transactions involve two unrelated entities, although transactions may occur between units of one entity (intercompany transactions). An intercompany transaction is a transaction that occurs between two units of the same entity. An intercompany transaction occurs when one unit of an entity transacts with another unit of the same entity. It is a transaction between two associated companies that file a consolidated tax return or financial statement.
Why intercompany transactions occur?
While these transactions can occur for a variety of reasons, they often occur as a result of the normal business relationships that exist between the units of the entity. These units may be the parent and a subsidiary, two subsidiaries, two divisions, or two departments of one entity.
It is common for vertically integrated organizations to transfer inventory among the units of the consolidated entity. On the other hand, a plant asset may be transferred between organizational units to take advantage of changes in demand across product lines. Intercompany transactions may involve such items as the declaration and payment of dividends, the purchase and sale of assets such as inventory or plant assets, and borrowing and lending.
Accounting Treatment for Intercompany Transactions:
An intercompany transaction is recognized in the financial records of both units of the entity as if it were an arms-length transaction with an unrelated party. From the consolidated entity’s perspective, the transaction is initially unrealized because unrelated parties are not involved; therefore, the intercompany transaction needs to be interpreted differently than it was by either of the participating units. The difference in interpretation generally results in the elimination of certain account balances from the consolidated financial statements.
The purpose of consolidated statements is to present, primarily for the benefit of the shareholders and creditors of the parent company, the results of operations and the financial position of a parent company and its subsidiaries essentially as if the group were a single company with one or more branches or divisions. Regardless of the type of transaction, the occurrence of an intercompany transaction, if not removed (eliminated) from the consolidated financial statements, will often result in a misrepresentation of the consolidated entity’s financial position.
- These transactions can occur for a variety of reasons and normally occur as a result of the normal business relationships between the units of the entity.
- An intercompany transaction is recognized in the financial records of both units of the entity as if it were an arms-length transaction with an unrelated party.
- These transactions might or might not be cash-settled.
- From the consolidated entity’s perspective, the transaction is initially unrealized because unrelated parties are not involved; therefore, the intercompany transaction needs to be eliminated from the consolidated financial statements.
Types of Intercompany Transactions:
Transactions between units of an entity can take several forms and can occur between any units of the entity. Transactions flowing from the parent to the subsidiary are commonly called downstream transactions, transactions from the subsidiary to the parent are commonly called upstream transactions, and transactions between subsidiaries are commonly called lateral transactions. Hence intercompany transactions can be classified as:
- Downstream Intercompany Transactions
- Upstream Intercompany Transactions
- Lateral Intercompany Transactions
Impact of Intercompany Transactions:
Interpreting the impact of intercompany transactions on the financial records of the units involved begins with understanding how the transactions are initially recognized on each unit’s financial records. Intercompany transactions need an effective system to manage them appropriately as it could be a complex affair for globalized companies. Some complexities are streamlining intercompany trading with unlimited trading partners, local statutory compliance with intercompany invoices for each of the trading partners, intercompany reconciliation, and transaction-level balancing for sub-ledger applications and intercompany eliminations at period close.
It is also important to understand how each intercompany transaction impacts the income statement and balance sheet of the units involved in the period of the intercompany transaction as well as in subsequent periods.
Intercompany V/s Intracompany Transactions:
Intercompany Transactions are between two or more related internal legal entities with common control, i.e. in the same enterprise. Intracompany transactions are between two or more entities within the same legal entity. Hence intercompany is cross legal entities and intracompany is across various units belonging to the same legal entity. Rules for intracompany processing can be determined by the organization based on internal procedures and guidelines, however, for intercompany transactions, companies need to follow the GAAP and the law.
Intercompany Reconciliations:
Intercompany reconciliations are required to ensure that balances owed to and from companies (legal entities) in the same group are in agreement so that when group accounts are prepared the intercompany balances all cancel out on consolidation. As organizations use multi-currency and different accounting systems, balances at business units or subsidiary companies may not match with each other and the yearend process can be delayed. Too many reconciling differences may require investigation or resolution before the balances are acceptable to management and/or auditors.
Some of the factors that give rise to intercompany differences are:
- Individual companies may book items to intercompany balances and not confirm with the other group company if they have recorded the other leg of the transaction.
- Wrong posting to/from intercompany accounts, may post balances due from other members of the group to sundry debtors or creditors
- Currency rate differences due to recording transactions on different dates may translate at different values when accounts are consolidated
- Summarization by aggregating amounts and posting them as a single journal when the counterparty posts amount individually
- Counterparties may be incorrectly identified by each other so that although the net positions are correctly stated overall the actual balance details do not eliminate
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
-
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
Reversing Journals are special journals that are automatically reversed after a specified date. A reversing entry is a journal entry to “undo” an adjusting entry. When you create a reversing journal entry it nullifies the accounting impact of the original entry. Reversing entries make it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the need for certain compound entries. See an example of reversing journal entry!
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
-
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved