- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Defining Organizational Hierarchies
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
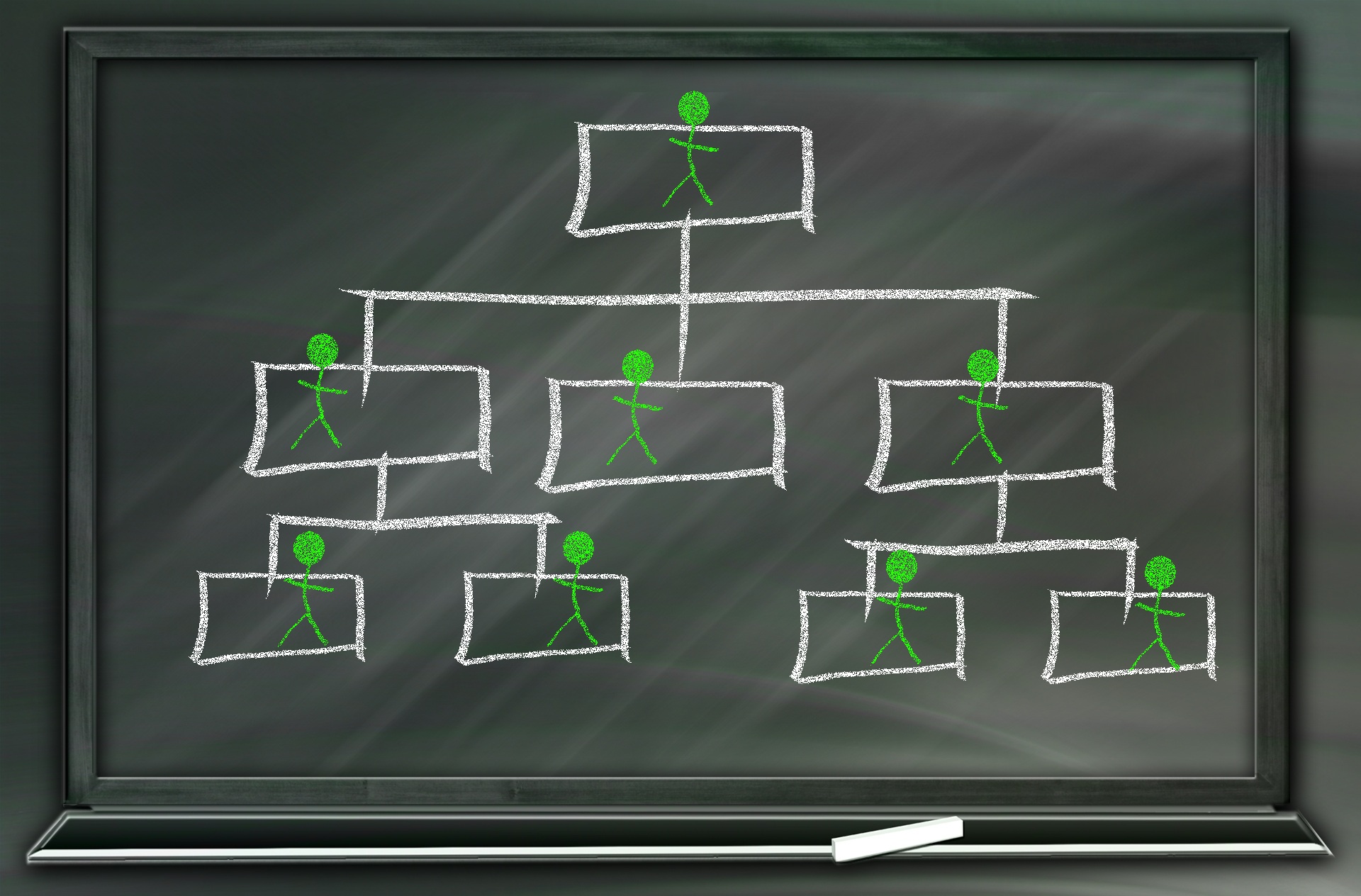
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
Meaning of Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints. These hierarchies need to be mapped to systems to ensure they are capturing the relevant business process information at relevant nodes to provide meaningful information for internal and external reporting.
Example
The account hierarchy allows you to map complex organizational structures of a business partner (for example, buying group, co-operative or chain of retail outlets). When you create a hierarchy structure, you form groups of business partners (for example, for purchasing groups). You can use them for statistical purposes and for marketing and accounting and other meaningful analyses.
Organizational hierarchies
Organizational hierarchies represent the relationships between the units/segments that make up your business.
Larger organizations may require some hierarchies that are based on business units and other hierarchies that are based on shared services, such as human resources and IT. They need to create cost centers in shared service departments and position them under business units, so that the costs of shared services are appropriately allocated. Now we will explore some examples of reporting needs arising out of these different hierarchies and dimensions. Any how they add complexity at transactional level to record relevant information appropriately.
Some areas where we need to deal with dimensions/hierarchies are:
Legal Structure
- Legal Entities
- Subsidiaries
- Tax Entities
- Statutory Entities
Operational Structure
- Business Units/Management Entity
- Divisions/Departments
- Business Functions
- Business Support Functions
- Organization Support Functions
- Cost Centers
- Profit Centers
- Business Employee Hierarchy
- Business Area /Project Area/ Controlling Area/ Product Lines/Service Lines
- Countries/Geography/Locations
- Accounts/Sub Accounts
Importance of Hierarchies
Defining organizational hierarchies enable to view and report on your business from different perspectives. You set up a hierarchy of legal entities for tax, legal, regulatory or statutory reporting. Various Legal entities can enter into legal contracts and are required to prepare statements that report on their performance. While performing business activities we need to capture and classify transactions at legal entity level to be able to identify transactions that belong to a specific legal entity. Therefore, there exists a need to define boundary at legal entity level to enable data classification, consolidation, security and reporting at these entity levels.
Example
A large corporate may create a central mailroom to receive all invoices from its vendors for which it need to make payment. These invoices are raised on separate legal entities within the same corporate group, but mailed to a central processing center for accounting and payment. The shared service resource who is working on these invoices must specify in the Accounting System the different legal entities to ensure proper treatment of these transactions. The payments should be issued from the respective bank accounts belonging to the legal entity on which the invoice has been raised.
You can create a hierarchy for purchasing function to control purchasing policies, rules, and business processes.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
-
Business Metrics for Management Reporting
Business metric is a quantifiable measure of an organization's behavior, activities, and performance used to access the status of the targeted business process. Traditionally many metrics were finance based, inwardly focusing on the performance of the organization. Businesses can use various metrics available to monitor, evaluate, and improve their performance across any of the focus areas like sales, sourcing, IT or operations.
-
Trial Balance in General Ledger
One of the greatest benefits of using a double-entry accounting system is the capability to generate a trial balance. What do we mean by trial balance? As the name suggests a trial balance is a report that must have its debits equals to credits. Understand the importance of trial balance and why it is balanced. Learn how it is prepared and in which format.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
-
Defining Organizational Hierarchies
A hierarchy is an ordered series of related objects. You can relate hierarchy with “pyramid” - where each step of the pyramid is subordinate to the one above it. One can use drill up or down to perform multi-dimensional analysis with a hierarchy. Multi-dimensional analysis uses dimension objects organized in a meaningful order and allows users to observe data from various viewpoints.
-
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
-
Reversing Journals are special journals that are automatically reversed after a specified date. A reversing entry is a journal entry to “undo” an adjusting entry. When you create a reversing journal entry it nullifies the accounting impact of the original entry. Reversing entries make it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the need for certain compound entries. See an example of reversing journal entry!
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved