- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Leadership Theories
- Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership Theories are well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations. Practical application is how to choose the right leadership approach for the situation. The theory emphasizes leader flexibility and advises leaders to flex their style based on the followers' needs. Leaders must adapt their leadership style to fit the prescribed task, understanding given situation/maturity of followers.
How does this Approach Works?
The situational approach is constructed around the idea that different employees are at different level of development or maturity stages which represents the relative competence and commitment of subordinates for a given task. For leaders to be effective in such situations, it is essential that they determine where subordinates are on the maturity levels and adapt their leadership styles so that their style matches with the style of the development level and the followers can be benefited by the time and energy spent by the leader on it. In a way this approach is mutually beneficial to both follower and the leader as leader can also save his time and energy by understanding the maturity levels of the follower.
It is designed to increase the frequency and quality of conversations about performance and development between managers and the people they work with so that competence is developed, commitment is gained, and talented individuals are retained. Highlighted below are the key learning objectives from this theory:
- Develop an understanding of Interaction Styles and how this model can assist in gaining a greater understanding of yourself and others
- Understand how your preferences can influence you and others
- Understand the importance of adapting own interaction style to increase effectiveness
- Be able to diagnose others’ development levels and choose the appropriate leadership style
- Know why there is no best leadership or coaching style
- Learn to use a common language for coaching and developing others
- Understand the negative impact of over supervision and under supervision on others’ performance and morale
Steps to Apply Situational Leadership Model:
1. Determine the nature of the situation.
2. Understand the nature and complexity of the task at hand
3. Evaluate the skills and the desire of the subordinates to do the task being asked to perform.
4. Identify correctly the specific developmental level at which their subordinates are functioning.
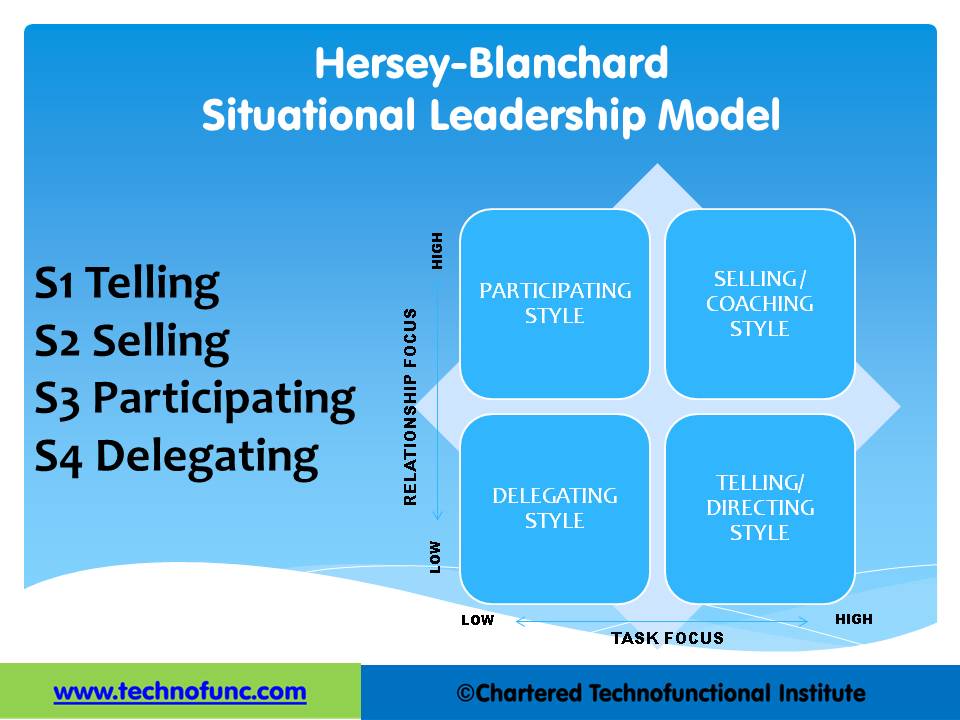
5. Adapt his or her style to the prescribed leadership style represented in the table given in the previous article.
Practical Applications of the Situational Approach:
- This theory is well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations.
- Perceived by organizations as an effective model for training people to become effective leaders and use the skills in workplace to solve common workplace conflicts.
- Highly practical, easy to understand, sensible theory that can be applied in a variety of settings and situations.
- Provide leaders with a valuable set of guidelines that can facilitate and enhance leadership.
- Emphasizes leader flexibility and recognizes that employees act differently with different tasks and leaders need to flex their style based on the situational or followers need.
- It is an encompassing model with a wide range of applications.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Participative Leadership Theories
Participative leadership theories rely on the involvement of different participants and suggest that the ideal leadership style is one that takes the inputs of others into account. Participative leaders encourage participation and contributions from group members and involve them in the decision-making process. Participative leadership tries to achieve through people, teamwork and collaboration.
-
The style approach emphasizes that one style of leadership behaviour cannot be effective in all situations. Earlier theories treated leadership exclusively as a personality trait and behavior approach has widened the scope by including the behaviors of leaders and what they do in various situations. Explore how you can benefit from the concepts to understand your own behaviors and what are some of the leadership tools based on the style approach to leadership.
-
Authentic leadership is a new approach to leadership in which leaders are genuine, self-aware, transparent, build honest relationships, and work on an ethical foundation. Authenticity is one of the core values of leadership. Authentic leaders have truthful self-concepts and they inspire by promoting openness by acting in a real, genuine, and sincere way. Authenticity requires self-awareness and the ability to act in accordance with one's true self.
-
Leadership Participation Inventory (LPI)
Kouzes and Posner introduced the Leadership Participation Inventory model of Transformational leadership. This model is also known as Kouzes and Posner's Leadership Challenge Model. They identified five practices of exemplary leadership - Model the Way, Inspire a Shared Vision, Challenge the Process, Enabling Others to Act, and Encourage the Heart.
-
Neo-Emergent Leadership theory supports that leadership is created through the emergence of information. Leaders can only be recognized after a goal is met. Follower’s perception of leaders is influenced by the ways these goals were accomplished.
-
According to the three-skill approach of Katz, the individual's leadership abilities vary depending on where leaders are in a management hierarchy. The practical implication of skills approach to leadership is that leaders can improve their capabilities in leadership skills through training and experience.
-
Investment Theory of Creativity
Sternberg in the year 2006, proposed the investment and confluence theory focused on understanding creativity. According to the investment theory, creativity requires a confluence of six distinct but interrelated resources known as intellectual abilities, knowledge, styles of thinking, personality, motivation, and environment. It emphasizes that creativity is not about one thing, but about a system of things.
-
Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership Theories are well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations. Practical application is how to choose the right leadership approach for the situation. The theory emphasizes leader flexibility and advises leaders to flex their style based on the followers' needs. Leaders must adapt their leadership style to fit the prescribed task, understanding given situation/maturity of followers.
-
Hawthorne Studies - Leadership
The Hawthorne studies were conducted on workers at the Hawthorne plant of the Western Electric Company by Elton Mayo and Fritz Roethlisberger in the 1920s. This study established the behavioral change that happened due to an awareness of being observed, resulting in active compliance with the supposed wishes of researchers, because of special attention received, or positive response to the stimulus being introduced.
-
Social learning theory is a theory of learning process that states that most human behavior is learned observationally through modeling. Behavior change can occur in response to leader modeling and learning occurs through the observation of rewards and punishments. The focus of this approach has been teaching leadership across formal and informal settings.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










