- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Communication Skills
- Leadership Traits – A great List
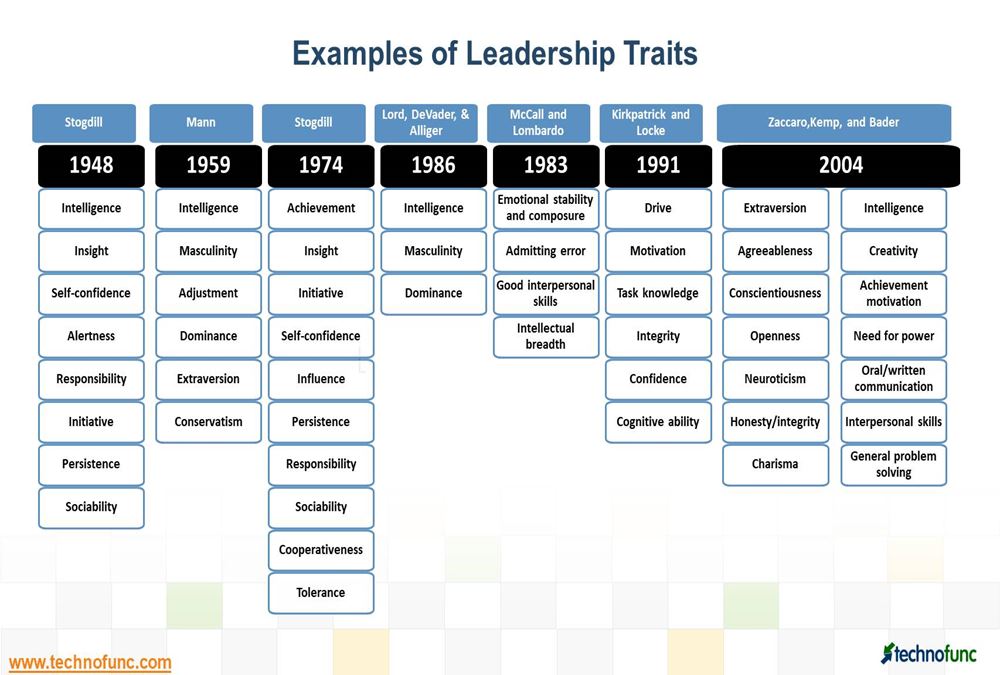
Leadership Traits – A great List
What are the qualities and characteristics of a good leader? Great leaders possess core leadership traits and skills. The list includes the most important leadership qualities and skills to look for in a great leader. These are must-have traits of a powerful and successful leader, the qualities a leader possess to be great.
A broad classification to six categories of traits is also done below:
Physical Characteristics of the Leader:
- Age
- Height
- Weight
- Alertness
- Energetic
- Masculinity
- High energy level
- Physical stamina
- Tolerance for stress
- Not concerned about being overworked
- Vitality
Background Characteristics of the Leader:
- Education
- Social Status
- Mobility
- Experience
- Experience in a variety of different types of situations
- Broader perspective
- Expertise in dealing with different types of problems
- Competent and skilled
Intelligence Characteristics of the Leader:
- Ability
- Judgment
- Knowledge
- Clever (intelligent)
- Conceptually skilled
- Creative
- Knowledgeable about group task
- Intellectual breadth
- Insight
- Learns from experience
- Adapts to change
- Good judgment
- Foresight
- Intuition
- Creativity
- Self-knowledge
- Coordinator
- Objective
- Decisive
- Asks for more responsibility
- Knows how to delegate
Personality/Emotional Characteristics of the Leader:
- Aggressiveness
- Alertness
- Dominance
- Decisiveness
- Enthusiasm
- Extroversion
- Independence
- Self-confidence
- Authoritarianism
- Assertive
- Tolerant of stress
- Conservatism
- Desire to improve
- Understands own strengths and weaknesses
- Self-objectivity
- Emotional intelligence
- Self-awareness
- Empathy
- Self-regulation
- Ambitious
- Courageous
- Knows self
- Risk taker
- Not intimidated by superiors
- Personal competence
- Optimistic
- Exhibits concern for others
- Encourages and engages opposing viewpoints
- Constant and reliable
- Self-disciplined
- Determination
- Need to achieve
- Caring
- Empathizing
- Constancy
Task-Oriented Characteristics of the Leader:
- Achievement Needs
- Responsibility
- Initiative
- Persistence
- Ambitiousness
- Achievement-orientated
- Decisive
- Persistent
- Willingness to assume responsibility
- Organized (administrative ability)
Social Characteristics of the Leader:
- Sociability
- Supervisory Ability
- Cooperativeness
- Popularity
- Prestige
- Tact
- Diplomacy
- Adaptability
- Adjustment
- Cooperative
- Dependable
- Tactful
- Persuasive
- Socially skilled
- Emotional stability and composure
- Good interpersonal skills
- Well-adjusted
- Oriented toward improving self
- Detached
- Honest
- Ethical
- Trustworthy
- Behavioral flexibility
- Understanding
- Empathy
- Social Insight
- Charm
- Tact
- Diplomacy
- Persuasiveness
- Listener
- Collaborative
- Strong motivator
- Cooperative
- Influencer
Communication:
- Ability to communicate
- Ability to articulate a vision
- Ability to persuade others
- Communicate purpose
- Communicate direction
- Communicates passion to others
- Good communication skills
- Use metaphors
- Experts at one-to-one communication
- Superior speakers
- Excellent writing skills
- Creates and maintains a communications network
- Has people keep them informed on problem situations
- Networks with people inside the organization
- Maintains contacts outside the organization
- Doesn’t depend on only one source for information
- Able to communicate with key individuals
- Eager to explore new approaches to their work
- Are not fuzzy about results, interested in ways to track their progress
- Communicates persuasively
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In emergent leadership, the leader is not appointed or elected to the leadership role but emerges as the leader as he is perceived by others over time as a result of the group's interaction. A person steps up as the leader over time by taking on tasks voluntarily, helping others complete their tasks better, and building consensus among groups.
-
There are four characteristics of leadership that help us to understand the character of leadership as a concept. 1. Leadership is a process, 2. Leadership involves influence, 3. Leadership always occurs in a group context and 4. Leadership involves goal attainment. These are the four components that make up the character of the 'leadership' term and help us to define the leadership concept. All of these components of leadership have common characteristics.
-
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
McGregor created Theory X and Theory Y of human work motivation and explained two styles of management known as authoritarian (Theory X) and participative (Theory Y). Theory X management assumes most people will attempt to avoid work whereas Theory Y managers trust their people to take ownership of their work.
-
The four theory of leadership was formulated after studying hundreds of leaders and the model includes four basic dimensions of effective leadership - support; interaction; facilitation; goal emphasis, and work facilitation. This model was tested as a predictor of an organization's effectiveness.
-
Participative Leadership Theories
Participative leadership theories rely on the involvement of different participants and suggest that the ideal leadership style is one that takes the inputs of others into account. Participative leaders encourage participation and contributions from group members and involve them in the decision-making process. Participative leadership tries to achieve through people, teamwork and collaboration.
-
The social identity theory of leadership views leadership as a group process. Social identity is a person's sense of who they are based on their group membership. Social identity theory sets agendas and goals generated by social categorization, defines who we are based on processes associated with social identity, and motivates to conduct ourselves based on what followers think of the leader.
-
The Leader-Member Exchange Theory (LMX), also called the Vertical Dyad Linkage Theory is a relationship-based approach that focuses on the two-way (dyadic) relationship to get the best from all team members. How leaders maintain their position in groups and develop an exchange with each of their subordinates. How leaders and members develop relationships that can contribute to growth or hinder development.
-
Transactional Analysis also is known as the theory of human personality was proposed by Eric Berne in the 1950s. This theory of transactional leadership defines three different ego states in a person who engages in transactions with another person's ego states. These three ego states refer to major parts of an individual's personality and reflect an entire system of thought, feeling, and behavior.
-
Self-leadership is a normative model of self-influence by the use of several behavioral strategies to gain a comprehensive self-influence perspective about oneself. Self-leadership is developing an understanding of your capabilities and abilities to influence your own communication, emotions, and behaviors to lead and influence others. Self-leadership is about personal growth and developing foresight.
-
Role theory is a concept in sociology and the role theory of leadership borrows these concepts to explain how people adapt to specific organizational and leadership roles. How the leaders and followers in an organizational context define their own roles, define the roles of others, how people act in their roles and how people expect people to act in their roles within the organization.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










