- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Leadership Theories
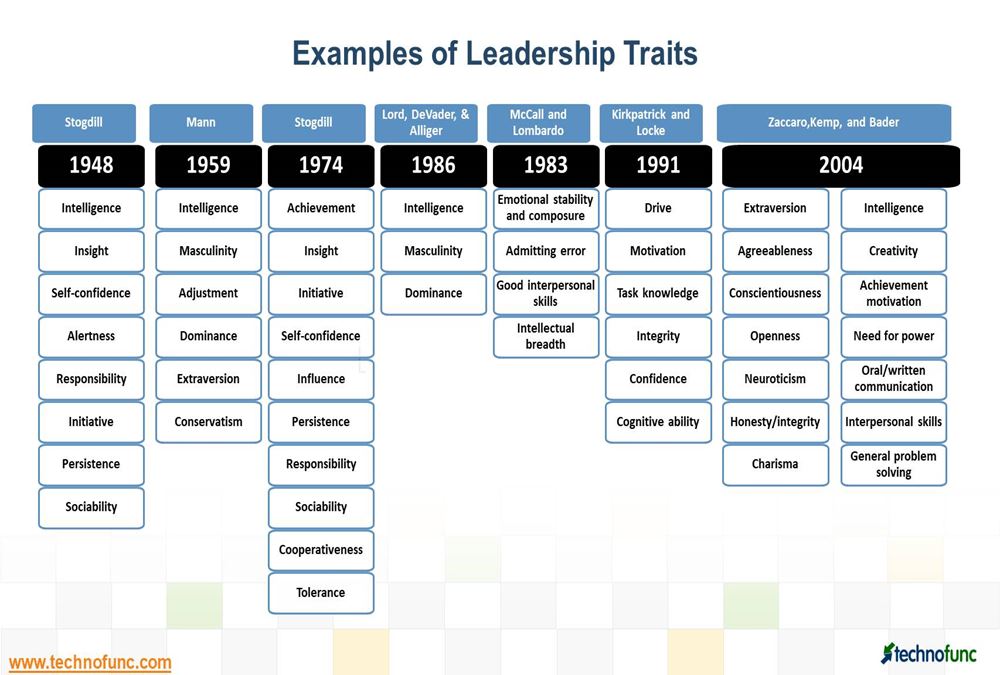
- Leadership Traits – A great List
Leadership Traits – A great List
What are the qualities and characteristics of a good leader? Great leaders possess core leadership traits and skills. The list includes the most important leadership qualities and skills to look for in a great leader. These are must-have traits of a powerful and successful leader, the qualities a leader possess to be great.
A broad classification to six categories of traits is also done below:
Physical Characteristics of the Leader:
- Age
- Height
- Weight
- Alertness
- Energetic
- Masculinity
- High energy level
- Physical stamina
- Tolerance for stress
- Not concerned about being overworked
- Vitality
Background Characteristics of the Leader:
- Education
- Social Status
- Mobility
- Experience
- Experience in a variety of different types of situations
- Broader perspective
- Expertise in dealing with different types of problems
- Competent and skilled
Intelligence Characteristics of the Leader:
- Ability
- Judgment
- Knowledge
- Clever (intelligent)
- Conceptually skilled
- Creative
- Knowledgeable about group task
- Intellectual breadth
- Insight
- Learns from experience
- Adapts to change
- Good judgment
- Foresight
- Intuition
- Creativity
- Self-knowledge
- Coordinator
- Objective
- Decisive
- Asks for more responsibility
- Knows how to delegate
Personality/Emotional Characteristics of the Leader:
- Aggressiveness
- Alertness
- Dominance
- Decisiveness
- Enthusiasm
- Extroversion
- Independence
- Self-confidence
- Authoritarianism
- Assertive
- Tolerant of stress
- Conservatism
- Desire to improve
- Understands own strengths and weaknesses
- Self-objectivity
- Emotional intelligence
- Self-awareness
- Empathy
- Self-regulation
- Ambitious
- Courageous
- Knows self
- Risk taker
- Not intimidated by superiors
- Personal competence
- Optimistic
- Exhibits concern for others
- Encourages and engages opposing viewpoints
- Constant and reliable
- Self-disciplined
- Determination
- Need to achieve
- Caring
- Empathizing
- Constancy
Task-Oriented Characteristics of the Leader:
- Achievement Needs
- Responsibility
- Initiative
- Persistence
- Ambitiousness
- Achievement-orientated
- Decisive
- Persistent
- Willingness to assume responsibility
- Organized (administrative ability)
Social Characteristics of the Leader:
- Sociability
- Supervisory Ability
- Cooperativeness
- Popularity
- Prestige
- Tact
- Diplomacy
- Adaptability
- Adjustment
- Cooperative
- Dependable
- Tactful
- Persuasive
- Socially skilled
- Emotional stability and composure
- Good interpersonal skills
- Well-adjusted
- Oriented toward improving self
- Detached
- Honest
- Ethical
- Trustworthy
- Behavioral flexibility
- Understanding
- Empathy
- Social Insight
- Charm
- Tact
- Diplomacy
- Persuasiveness
- Listener
- Collaborative
- Strong motivator
- Cooperative
- Influencer
Communication:
- Ability to communicate
- Ability to articulate a vision
- Ability to persuade others
- Communicate purpose
- Communicate direction
- Communicates passion to others
- Good communication skills
- Use metaphors
- Experts at one-to-one communication
- Superior speakers
- Excellent writing skills
- Creates and maintains a communications network
- Has people keep them informed on problem situations
- Networks with people inside the organization
- Maintains contacts outside the organization
- Doesn’t depend on only one source for information
- Able to communicate with key individuals
- Eager to explore new approaches to their work
- Are not fuzzy about results, interested in ways to track their progress
- Communicates persuasively
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Power is the ability to exercise influence or control over others. Leadership involves authority and it is very important for leaders to understand what type of power they're using. The 5 Types of Power in Leadership are Coercive power, expert power, legitimate power, referent power, and reward power. Authority is the right to command and extract obedience from others. It comes from the organization and it allows the leader to use power.
-
In the field of communication studies, there are numerous models. No one model is suitable for all purposes and all levels of analysis. Some common models are known as Lasswell Model, George Gerbner Model, David Berlo Model, Shanon and Weaver Model, Osgoods Model, and Schramm Model. All these describe the four components of the communication process, namely, the source (communicator), the message, the channel, the receiver (audience).
-
The Fiedler Model of leadership is a contingency theory and states that a leader's effectiveness is based on the situation. There is no one best style of leadership and the effectiveness of a leader in an organization depends on matching the leader to the situation. Leaders should determine the natural leadership style and assess the situation to flex the style.
-
Trait theories of leadership identify the specific personality traits that distinguish leaders from non-leaders. The trait model of leadership is based on the traits or characteristics of leaders that make them successful in their leading role. These theories use heritable attributes to predict leadership effectiveness.
-
Neo-Emergent Leadership theory supports that leadership is created through the emergence of information. Leaders can only be recognized after a goal is met. Follower’s perception of leaders is influenced by the ways these goals were accomplished.
-
Symbolic Interaction and Social Change
George Herbert Mead, an American philosopher, affiliated with the University of Chicago founded the theory of symbolic interactionism. A major aspect of this is that people interact by symbols both verbal and non-verbal signals and every interaction makes a contribution to the mental make-up of the mind thus every interaction with someone, changes you and you go away a different person signifying that humans and change go together.
-
Burns Transformational Leadership Theory
Transformational leadership theory has been defined by James MacGregor Burns as a process where both leaders and followers mutually raise one another to higher levels of morality and motivation. The concept of transforming leader works with teams to garner trust, respect, and admiration while reaching to higher moral positions. The transformational theory of leadership was developed while studying political leaders and how they use charismatic methods to attract people to the values.
-
Situational Theories of Leadership
The situational theories of leadership assume that the most effective style of leadership depends from situation to situation. Situational leadership is a leadership style in which the leader must adjust to match the development needs of the followers. They must adapt varying behaviors to strike the right balance between task & relationship based on different levels of maturity of followers and also as followers develop and cultivate their skills.
-
University of Iowa Studies was the first leadership study to analyze leadership using scientific methodology. The study was conducted by Lewin, Lippitt, and White and worked on different styles of leadership. The studies explored three leadership styles - authoritarian, democratic, and laissez-fair leaders. This early study was very influential and established three major leadership styles.
-
Behavioral Theories of Leadership
Behavioral Theory of leadership is a big leap from Trait Theory, as it was developed scientifically by conducting behaviour focused studies. The theory emphasizes that leadership capability can be learned, rather than being inherent. This theory is based on the principle that a leader's behaviors can be conditioned in a manner that one can have a specific response to specific stimuli.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved