- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Concept of Representative Office
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature. As its name says, a representative office represents its foreign parent in the country of operations.
A representative office is an office established by a company to conduct marketing and other non-transactional operations, generally in a foreign country where a branch office or subsidiary is not warranted. A representative office cannot regularly buy and sell goods or offer services. Representative offices are generally easier to establish than a branch or subsidiary, as they are not used for actual "business" (e.g. sales) and therefore there is less incentive for them to be regulated.
A representative office is a more tentative step into the foreign market, often used by investors to test the waters or for promotional purposes when the business distributes its goods by other means. A representative office is most appropriate in the early stages of corporation’s business presence in a foreign country. They have been used extensively by foreign investors in emerging markets such as China, India and Vietnam although they do have restrictions through not being able to invoice locally for goods or services.
Main Features:
- Representative office to engage only in activities which do not amount to, or form part of, the carrying on of the relevant business in foreign country.
- Having a nominated person employed by a local affiliate to handle enquiries could fall into this category.
- The representative office can contact customers and enter into contracts on behalf of its foreign parent, but can’t sell the goods itself.
- Representative Offices tend to be utilized by foreign investors in fields such as sourcing of products, quality control, and general liaison activities between the Head Office and the Representative Offices overseas.
- Corporations should periodically review the suitability of the structure and its activities to make sure that the company is not triggering a taxable presence in the foreign land by exceeding the permissible activities.
ICICI Bank, India's second largest bank, opened representatives offices in three east-Asian countries Thailand, Indonesia and Malaysia". The branches are expected to enable the bank to increase its participation in India's trade transactions in the region. It also has a representative office in the US.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
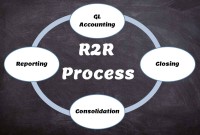
Record to report (R2R) is a finance and accounting management process that involves collecting, processing, analyzing, validating, organizing, and finally reporting accurate financial data. R2R process provides strategic, financial, and operational feedback on the performance of the organization to inform management and external stakeholders. R2R process also covers the steps involved in preparing and reporting on the overall accounts.
-
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
-
In this article, we explain some commonly used subsidiary ledgers like accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, accounts payable subsidiary ledger or creditors' subsidiary ledger, inventory subsidiary ledger, fixed assets subsidiary ledger, projects subsidiary ledger, work in progress subsidiary ledger, and cash receipts or payments subsidiary ledger.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
-
An organizational design is the process by which a company defines and manages elements of structure so that an organization can control the activities necessary to achieve its goals. Good organizational structure and design helps improve communication, increase productivity, and inspire innovation. Organizational structure is the formal system of task and activity relationships to clearly define how people coordinate their actions and use resources to achieve organizational goals.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
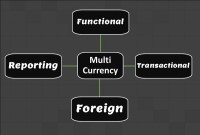
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
Learn the typical accounting cycle that takes place in an automated accounting system. We will understand the perquisites for commencing the accounting cycle and the series of steps required to record transactions and convert them into financial reports. This accounting cycle is the standard repetitive process that is undertaken to record and report accounting.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved