- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Concept of Foreign Branches
Concept of Foreign Branches
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
A branch office refers to an establishment which carries on substantially the same business and activity as is carried out by its Head Office. Foreign Branch of a company refers to the branch of a company that operates in the foreign country. It is a branch of a company operating outside the country of its registration.
Some attributes of foreign branch offices are:
- Does not require opening a separate legal entity in the country of operations
- The branch is legally part of the company and is not a separate entity
- The range of the activities that can be undertaken, substantially increase as compared to a representative office
- Branches generally a constitute taxable presence in a foreign country and must account for and file prescribed returns with the local authorities
- Attributing the profits to the branch activities require arm’s length transaction
- Foreign branch is subject to special tax considerations.
- A subsidiary of a foreign corporation generally is taxed as any other domestic corporation, that is, as a separate taxable entity apart from its foreign parent. In contrast, a branch of a foreign corporation is not treated as a separate taxable entity; instead, the code and regulations employ a set of special rules to determine the tax liability of the branch both in domestic country and foreign country of operations.
Such branch offices help the company in:
- Spreading its business to diverse locations and thus increasing the customer base
- Expanding the size of the market for a company's product by attracting more customers
- Bringing its product closer to the customers by increasing their accessibility to it
- Making the distribution and marketing of its goods and services easier and more effective
- Widening the scope of its trading and manufacturing activities
- Bringing more opportunities and opening unexplored avenues
- Fuel the growth of the company
- Enhance its profitability
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
In every journal entry that is recorded, the debits and credits must be equal to ensure that the accounting equation is matched. In this article, we will focus on how to analyze and recorded transactional accounting information by applying the rule of credit and debit. We will also focus on some efficient methods of recording and analyzing transactions.
-
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
-
Accrued expenses, sometimes referred to as accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts. Discuss the need to record accrued liabilities and why they require an adjustment entry. Understand the treatment for these entries once the accounting period is closed and learn to differentiate when the commitments become liabilities.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
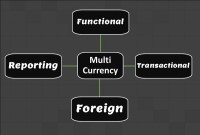
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
Divisional Organizational Structures
The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
-
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
-
Matrix Organizational Structures
In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved