- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Leadership Theories
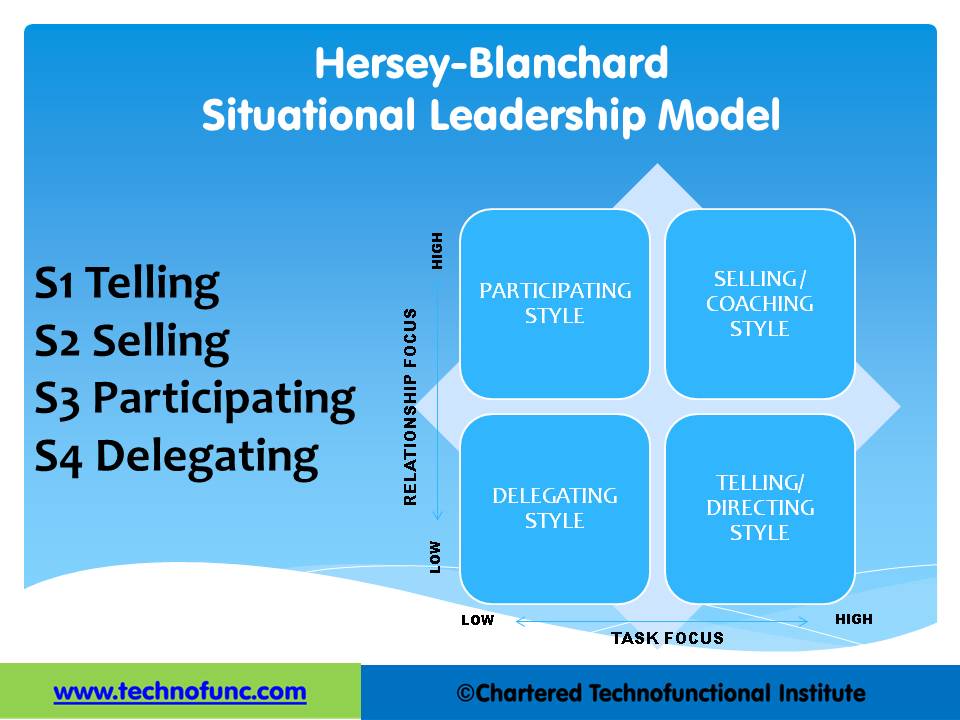
- Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership - Application
Situational Leadership Theories are well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations. Practical application is how to choose the right leadership approach for the situation. The theory emphasizes leader flexibility and advises leaders to flex their style based on the followers' needs. Leaders must adapt their leadership style to fit the prescribed task, understanding given situation/maturity of followers.
How does this Approach Works?
The situational approach is constructed around the idea that different employees are at different level of development or maturity stages which represents the relative competence and commitment of subordinates for a given task. For leaders to be effective in such situations, it is essential that they determine where subordinates are on the maturity levels and adapt their leadership styles so that their style matches with the style of the development level and the followers can be benefited by the time and energy spent by the leader on it. In a way this approach is mutually beneficial to both follower and the leader as leader can also save his time and energy by understanding the maturity levels of the follower.
It is designed to increase the frequency and quality of conversations about performance and development between managers and the people they work with so that competence is developed, commitment is gained, and talented individuals are retained. Highlighted below are the key learning objectives from this theory:
- Develop an understanding of Interaction Styles and how this model can assist in gaining a greater understanding of yourself and others
- Understand how your preferences can influence you and others
- Understand the importance of adapting own interaction style to increase effectiveness
- Be able to diagnose others’ development levels and choose the appropriate leadership style
- Know why there is no best leadership or coaching style
- Learn to use a common language for coaching and developing others
- Understand the negative impact of over supervision and under supervision on others’ performance and morale
Steps to Apply Situational Leadership Model:
1. Determine the nature of the situation.
2. Understand the nature and complexity of the task at hand
3. Evaluate the skills and the desire of the subordinates to do the task being asked to perform.
4. Identify correctly the specific developmental level at which their subordinates are functioning.
5. Adapt his or her style to the prescribed leadership style represented in the table given in the previous article.
Practical Applications of the Situational Approach:
- This theory is well known and frequently used for training leaders within organizations.
- Perceived by organizations as an effective model for training people to become effective leaders and use the skills in workplace to solve common workplace conflicts.
- Highly practical, easy to understand, sensible theory that can be applied in a variety of settings and situations.
- Provide leaders with a valuable set of guidelines that can facilitate and enhance leadership.
- Emphasizes leader flexibility and recognizes that employees act differently with different tasks and leaders need to flex their style based on the situational or followers need.
- It is an encompassing model with a wide range of applications.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Socio-technical theory of leadership focus on the presence of two subsystems in every organization, the interrelatedness of social and technical aspects of an organization. Theory pertains to the social aspects of people and technical aspects of an organization, which means structure and processes within the organization.
-
In the field of communication studies, there are numerous models. No one model is suitable for all purposes and all levels of analysis. Some common models are known as Lasswell Model, George Gerbner Model, David Berlo Model, Shanon and Weaver Model, Osgoods Model, and Schramm Model. All these describe the four components of the communication process, namely, the source (communicator), the message, the channel, the receiver (audience).
-
Leadership traits refer to personal qualities that define effective leaders. Here are the major leadership qualities that can make someone a good leader. Five key traits that are common in leaders can be learned and sharpened with time.
-
The Systemic Approach to Leadership
The systemic approach to leadership looks at the organization as a whole and focuses on the understanding of the organization as a system. Moving to systems thinking demand managers to view organizations as organic systems. Leaders are also part of this complex system which is constantly undergoing change and evolving. The leaders need to manage the relations and networks within these systems by acting with systemic awareness.
-
Situational Theories of Leadership
The situational theories of leadership assume that the most effective style of leadership depends from situation to situation. Situational leadership is a leadership style in which the leader must adjust to match the development needs of the followers. They must adapt varying behaviors to strike the right balance between task & relationship based on different levels of maturity of followers and also as followers develop and cultivate their skills.
-
Trait theories of leadership explain the leadership traits that have been studied to determine what makes certain people great leaders. The practical application of the theory is looking at how the leader‟s behavior affects their subjects.
-
University of Iowa Studies was the first leadership study to analyze leadership using scientific methodology. The study was conducted by Lewin, Lippitt, and White and worked on different styles of leadership. The studies explored three leadership styles - authoritarian, democratic, and laissez-fair leaders. This early study was very influential and established three major leadership styles.
-
Contingency Theories in Action
Contingency theory suggests matching the best leader to a specific situation based on situational factors and the leadership style. The practical application of theory can be done in various ways. The workplace example is to determine the best candidate for a given set of requirements using the LPC score. Applying the model to determine a leader's ability to adapt in the scenario of a new project etc..
-
The Path-Goal theory defines the characteristics of followers and organizational context and the corresponding leadership style best suited to these factors. A leader should adapt to a behavior that is most relevant for a given employee and work environment mix to achieve a goal. The application of theory drives increased employees' motivation, empowerment, and satisfaction resulting in increased productivity.
-
The great man theory of leadership is a 19th-century idea that states a person is either a natural-born leader or not. Some people are born with the necessary leadership attributes that help them create a great impact on society, politics, or the military. The theory focuses on identifying the innate qualities and characteristics possessed by great men.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved