- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- Procure to Pay
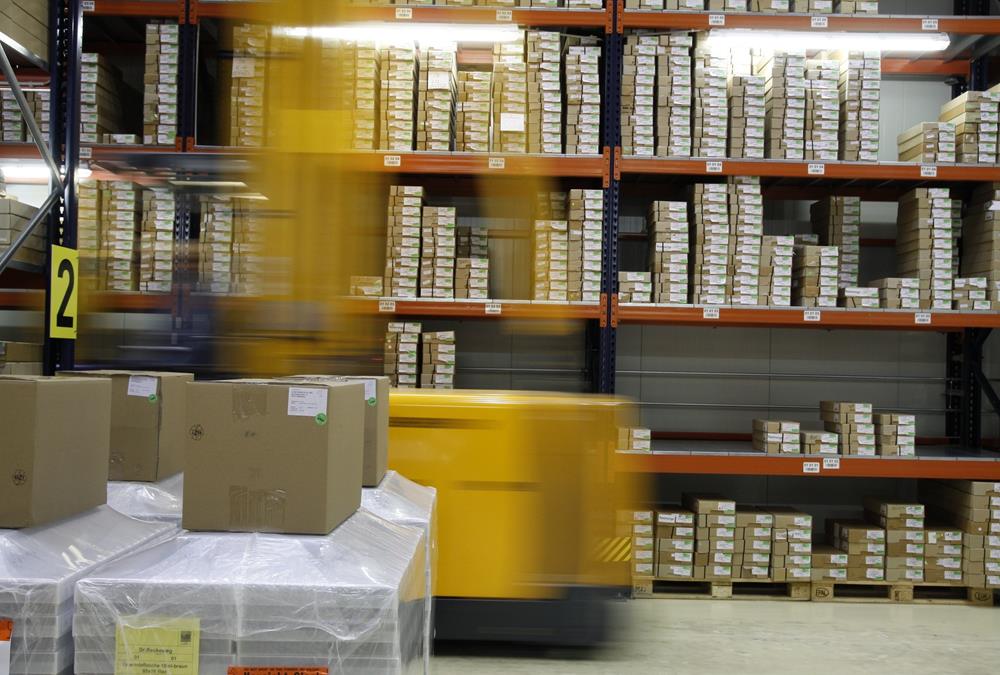
- Warehouse Packaging Process
Warehouse Packaging Process
Before shipping, businesses need to make sure that the items will arrive in good condition. Packaging is a form of protection against environmental threats that the product will face from the time it leaves warehouse facility until the time it reached the customer. The packaging is intended to provide protection for the item as it is being handled in the warehouse or when the item is being shipped.
What is Packing?
Before shipping, businesses need to make sure that the items will arrive in good condition. Packaging is a form of protection against environmental threats that the product will face from the time it leaves warehouse facility until the time it reached the customer. The packaging is intended to provide protection for the item as it is being handled in the warehouse or when the item is being shipped. In this process, warehouse workers pick products from the storage locations and move them to a packing station where they check the item quantities and types, and assign them to appropriate containers. When a container is fully packed, they can close it and move it to the outbound docks, and the products are ready to ship.
Packing Process
The packing process allows you to validate and pack products into containers. Packing in a warehouse depends on the way the inventory is picked and the reference available to the packer. Packing also depends on the containerization process. Once an order is picked, it is handed off to a packer. The packer is responsible for securely placing the items in a box or poly mailer, adding in any needed packing materials, and putting a shipping label on it.
Packaging Product Dimensions
Before items can be stored or packed efficiently, warehouse management system need to understand and define packaging product dimensions for each of the product. Each dimension type provides a set of physical measurements (weight, width, depth, and height), and establishes the process where those physical measurement values apply.
Some examples of packaging dimensions are given below:
Storage Storage dimensions: are used along with location volumetric to determine how many of each item can be stored in various warehouse locations.
Packing Packing dimensions: are used during containerization and the manual packing process to determine how many of each item will fit in various container types.
Nested Packing: Nested packing dimensions are used when the packing process contains multiple levels.
Shipping Dimensions Shipping dimensions of the product may be different from actual, laid out dimensions. Shipping dimensions refer to the size of the item or package when it will be shipped. This may include extra padding or wiggle room required.
Packaging Types
There are different types of packaging that are used for finished goods; internal packaging and external packaging. The external packaging must be sufficient to protect the internal packaging as well as the finished item. The external packaging should have dimensions that allow a suitable quantity to be stored on a pallet most efficiently. Choosing the right packaging for a shipment depends on the products, the shipping method, and the destination. The right packaging method is the one that ensures that your product arrives in good condition for the lowest cost.
- By far the most common form of packaging is cardboard, also known as corrugated fiberboard or just corrugate. Corrugate is cheap, strong, and light, so it’s the perfect material for packaging all kinds of products.
- Some products can still get damaged if they move around inside a cardboard box, however. One solution is to add filler materials such as packing paper, packing peanuts, or bubble wrap.
- If the products you’re shipping are sensitive to moisture, there may be a need to use an anticorrosion coating, special wrapping, or moisture-absorbing packets.
- Electronic products are sensitive to static electricity, so these products require special protection against electrostatic discharge.
Packing Materials and Fees
Packing material fees are paid to vendor company based on per unit of weight, for each material that a packing unit consists of. Packing material weights and fees are calculated for sales order lines and purchase order lines. Packing Cost is calculated based on type of packing material and price of same for a specific period.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Warehouse management and distribution logistics involve the physical warehouse where products are stored, as well as the receipt and movement of goods takes place. Warehouse management aims to control the storage and movement of products and materials within a warehouse. These operations include the receipting of inwards goods, tracking, stacking and stock movement through the warehouse.
-
Types of Inventory Count Processes
While dealing with lots of inventory in a warehouse, lots of things can go wrong. Shipments may not have the right number of units in them, or they could get damaged somewhere along the supply chain. Discrepancies in the stock may arise as part of every inventory control, and need to be corrected immediately after the inventory control procedure has been finished.
-
Types of Order Picking Methods in the Warehouse
There are many different types of picking in a warehouse and each one works as a customized solution for each business. Depending on the size of your warehouse and inventory, the manpower you have on hand, and the number of customer orders made each day, there may be certain methods that are more efficient for you than others.
-
To stay competitive in today’s tough market, the location of your warehouse is vital. To grow retail business need to offer to customers faster and affordable shipping time, which is dependent on the warehousing location as the location of the warehouse affects the transit time to ship orders to customers.
-
In the normal course of business, customers are likely to return orders from time to time due to various reasons and business should design processes the manage and accept such returns. A well designed returns management process can reduce costs and issues associated with returns or exchanges.
-
Warehouses can be places where piles of packed or loose products occupy space. If left disorganized, it will become very challenging to identify products for packing or picking. Hence, proper organization of warehouse is very important. Warehouse labeling systems eliminate this problem by making sure products are easily identified and managed during the warehousing and shipping process. Labeling is the most functional and cost-effective way to keep your warehouse organized and operating efficiently.
-
Overview of Warehouse Processes
The basic function of a warehouse is to store goods. This means that they receive deliveries from suppliers, do any necessary checking and sorting, store the materials until it is dispatched to customers. Traditionally warehouses were seen as places for the long-term storage of goods. Now organizations want to optimize their customer experience and try to move materials quickly through the supply chain, so the role of warehousing has changed.
-
What is the difference between Warehouse Management & Inventory Management?
The terms “inventory management” and “warehouse management” are sometimes mistakenly used interchangeably as they both deal with operations and products of industries. Despite their few similarities, there are many notable differences between warehouse and inventory management systems.
-
When a customer wants a product that has been stored in the warehouse, the same need to be picked off the shelf (or off the floor) and get it ready for shipping. Depending on how big is the warehouse, picking can take a while. (Many distribution centers cover more than 1 million square feet.). Hence, warehouse order picking methods are an important aspect within any warehouse.
-
Transport operations are often divided into full load and part load and due to economies of scale, the unit costs are higher for part loads. Our customer needs several part loads delivering, so it can reduce costs by consolidating these into full loads. Then it gets all the part loads delivered to a warehouse near the suppliers, consolidates them into full loads, and pays the lower costs of full-load transport to its operations.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved