- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
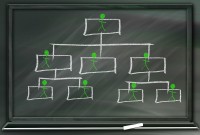
- Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-Based Organizational Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
Team Based Structure
Team-based structure is a relatively new structure that opposes the traditional hierarchical structure and it slowly gaining acceptance in the corporate world. In such a structure, employees come together as team in order to fulfill their tasks that serve a common goal.
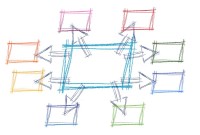
Network of Teams - The Agile Model
Agile organizations are characterized as a network of teams operating in rapid learning and decision-making cycles. Traditional organizations place their governance bodies at their apex, and decision rights flow down the hierarchy.
In case of network of teams the focus of organization structure will shift from hierarchy management structures to networks and teams who work closer to the customer base, having more control over decision making. In case of agile organizations teams work towards accomplishment of a common purpose and use new data to give decision rights to the teams closest to the information. An agile organization can ideally combine velocity and adaptability with stability and efficiency. These teams are cross functional, mission based working towards driving business outcomes.
Main Features
- Cross functional and self managing teams
- Shared purpose & vision
- Flexible resource allocation
- Clear accountability
- Iteration and experimentation
- Faster problem-solving and decision making
- Team collaboration results in higher productivity and performance
- Challenges around career path definition
This kind of an agile organization is quick to respond to changes within the market by making fast decision cycles, has the ability to efficiently deal with new threats from internal/external factors and can keep abreast of the fast advancements of technology, enabling businesses to succeed in a turbulent environment of constant change.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
McKinsey 7S Framework is most often used as an organizational analysis tool to assess and monitor changes in the internal situation of an organization. The model is based on the theory that, for an organization to perform well, seven elements need to be aligned and mutually reinforcing.
-
Legal Structures for Multinational Companies
A multinational company generally has offices and/or factories in different countries and a centralized head office where they coordinate global management. A multinational company (MNC)is a corporate organization that owns or controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
-
What is Accounting & Book Keeping
Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of everyday transactions. Each day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; however, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved