- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Career Management
- Emergent Leadership
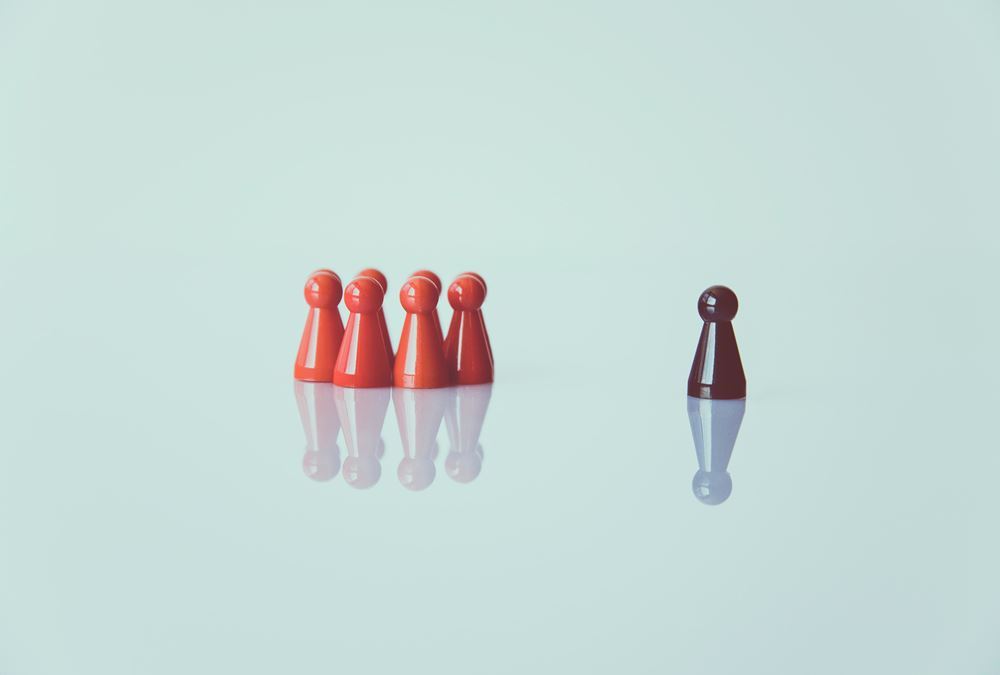
Emergent Leadership
Emergent leadership occurs when a group member is not appointed or elected as leader, but rather that person steps up as the leader over time within-group interactions. Have you ever faced challenges in getting accepted into your new role of position as a leader? Groups don't automatically accept a new "boss" as a leader. Emergent leadership is what you must do when taking over a new group. Learn more about emergent leadership.
What is Emergent Leadership?
Have you ever noticed that the person who has been assigned to a leadership position does not always become the real leader in spite of having a formal leadership position in an organization? Similarly there exist informal leaders because of the way they are treated, their commands and directions followed, the respect they command, the way other group members respond to them. When others perceive an individual as the most influential member of a group or an organization, regardless of the individual’s title, the person is exhibiting emergent leadership. How a group member emerges and maintains a leadership position, has been a subject of study for more than a century now and since then various phenomena, theories, and techniques of emergent leadership have been identified, developed, and advocated. The individual acquires emergent leadership through the support and acceptance of other people in the organization and it is the “emergent leader” who is most respected and most followed in any leadership setting.
Theories on Emergent Leadership:
1. Valence model of Emergent Leadership:
This model is based on Tuckman's (1965) group-development sequence proposed by Stein, Hoffman, Cooley, & Pearse in 1979. According to this model, the process of emergent leadership passes through three distinct stages; Orientation, Conflict, and Emergence. During the orientation stage potential leaders announce their candidature, during the conflict stage there is more than one leader competing for the same emergent leadership position and finally, in the emergence stage, group members willingly start following and obeying the leader who has passed the "emergence threshold."
2. Theory of Idiosyncrasy Credit:
This theory was proposed by Hollander (1958, 1961) where he theorized that the group member who emerges as the leader is perceived by other group members as meeting expectations that the group has for the leader. The more leaders are believed to meet the groups' expectations, the more leaders accumulate credits. Thus, leaders both assert their influence and have their influence accepted as a result of the credits they earn. If the leader does not innovate and does not conform in accordance with the group's expectations, the leader will lose credits. If enough credits are lost, then the leader can be replaced by another group member.
3. Social Identity Theory:
This theory provides a unique perspective on leadership emergence. According to this theory, leadership emergence is the degree to which a person fits with the identity of the group as a whole. As groups develop over time, a group prototype also develops. Individuals emerge as leaders in the group when they become most like the group prototype. Being similar to the prototype makes leaders attractive to the group and gives them influence with the group.
4. Neo-Emergent Theory:
The neo-emergent leadership theory (from the Oxford school of leadership) supports that leadership is created through the emergence of information by the leader or other stakeholders, not through the true actions of the leader himself. Leaders can only be recognized after a goal is met, and that follower’s perception of leaders is heavily influenced by the accounts of how those goals were accomplished.
Characteristics of Emergent Leadership:
1. This type of leadership emerges over a period through communication, they are outspoken and perceived by others as contributing great ideas
2. Emergent Leaders are verbally involved with their team members
3. Emergent Leaders seek others’ opinions, are innovative, and seek new ideas
4. Emergent Leaders are more dominant, more intelligent, and more confident about their own performance
Conclusion:
Emergent leadership is a leadership style that is based on creating a collaborative culture that is proven to dramatically increase innovation and profit. Emergent Leaders are armed with persistence and effective communication skills which help them get involved with people, seek information firsthand, and be innovative taking inputs from the entire group. This form of leadership is more adaptable to change and emergent leaders are more effective and have a greater chance of succeeding in any setting.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Authoritarian Leadership Style
Although generally considered as a traditional, outdated, and non-preferred style of leadership, the autocratic style still can be used effectively in certain situations. It is a leadership style characterized by individual absolute control over a group. If you work for an autocratic leader, your job is usually to do what you're told. Learn more about this style and situations where this could be an effective style to use and when to avoid this type of approach. Analyze the characteristics of this style to evaluate if your followers consider you an authoritarian leader!
-
Understanding of how individuals of different cultures interact with each other is very important. Not all individuals can adapt to the leadership styles expected in a different culture whether that culture is organizational or national. In a fast-paced business environment, developing a richer understanding and sensitivity to other cultures is a skill that leaders must possess. Learn to be effective in a cross-cultural setting.
-
Charisma is a certain quality of an individual personality, by virtue of which he is set apart from ordinary men. Charismatic Leader gathers followers, through dint of personality and charm. Understand the meaning and concept of Charismatic Leadership and the qualities of a charismatic leader. Gain an understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of using charismatic leadership. Finally, explore the difference between charismatic and transformational leadership.
-
Collaborative leadership is all about collaborative problem-solving and decision-making or can also be defined as the leadership of a collaborative effort. . The term started to appear in the mid-1990s in response to the formation of long term public-private partnerships to rebuild public infrastructure. Learn how you can use principles of collaborative leadership to enhance your leadership skills for being an effective leader.
-
Frederick Winslow Taylor started the “Scientific Management Movement”, and attempted to study the work process scientifically. Scientific management, also called Taylorism, was a theory of management that analyzed and synthesized workflows. It is a system for increasing the efficiency of manpower to its maximum potential and streamlining production to improve efficiency. This article explores this theory in more detail.
-
Charles Darwin had once commented that “It is not the strongest or the most intelligent who will survive but those who can best manage change.” Agility means the capability of rapidly and efficiently adapting to changes and recently, agility has been applied in the context of software development, agile enterprise, and agile leadership. Agile leaders play an important, even essential, role in scaling agility in an organization. Understand how being an agile leader helps in effectively catalyzing organizational change.
-
Laissez-faire is a style of leadership that affords the group members a great deal of independence. Tasks are delegated to the group members and they are responsible to see the project through to fruition. Research has shown that this style of leadership leads to the lowest levels of productivity. This article explains this style and covers the implications of having a hands-off approach and the situations where this style could be effective.
-
Facilitative Leadership is all about involving the employees in the decision-making process at all levels enhancing their sense of ownership, responsibility, and motivation. Facilitative leadership style uses a number of indirect communication patterns to help the group reach consensus and build commitment for the decision taken. To be effective in modern organizations, managers need to become facilitative leaders, learn what it means to be a one.
-
Crisis leadership is a very important part of leading in today's world. The skills a leader needs in order to guide people during a crisis are different from the skills needed to help a group grow. Are you a good crisis leader? What is your leadership style in case of a business crisis situation? A business crisis can test the strongest of leaders, read this article to explore how to ensure you’re ready to take action and weather the storm when one strikes you.
-
We define Lean as the systematic elimination of waste through a continual effort to decrease inefficiency; the lean leader strives to create a more efficient organization. Lean leadership is a philosophy. It is a consistent way of thinking and being in your role as a leader. The focus of this approach is on raising new leaders and help their team embrace a culture of continuous improvement. Learn what we mean by lean leadership style and its principles.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved