- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Leadership & Management
- Management Theories
Management Theories
Management theories are the recommended management strategies that enable us to better understand and approach management. Many management frameworks and guidelines were developed during the last four decades.
What do we mean by Management Theories?
Management theories are the set of general rules that guide the managers to manage an organization. Management theories (also known as "Transactional theories") focus on the role of supervision, organization, and group performance. Theories are an explanation to assist employees to effectively relate to the business goals and implement effective means to achieve the same. In this article, we will discuss the historical context of management, diverse views on management, and finally the theories of management.
Early management theories base leadership on a system of reward and punishment. Managerial theories are often used in business; when employees are successful, they are rewarded; when they fail, they are reprimanded or punished.
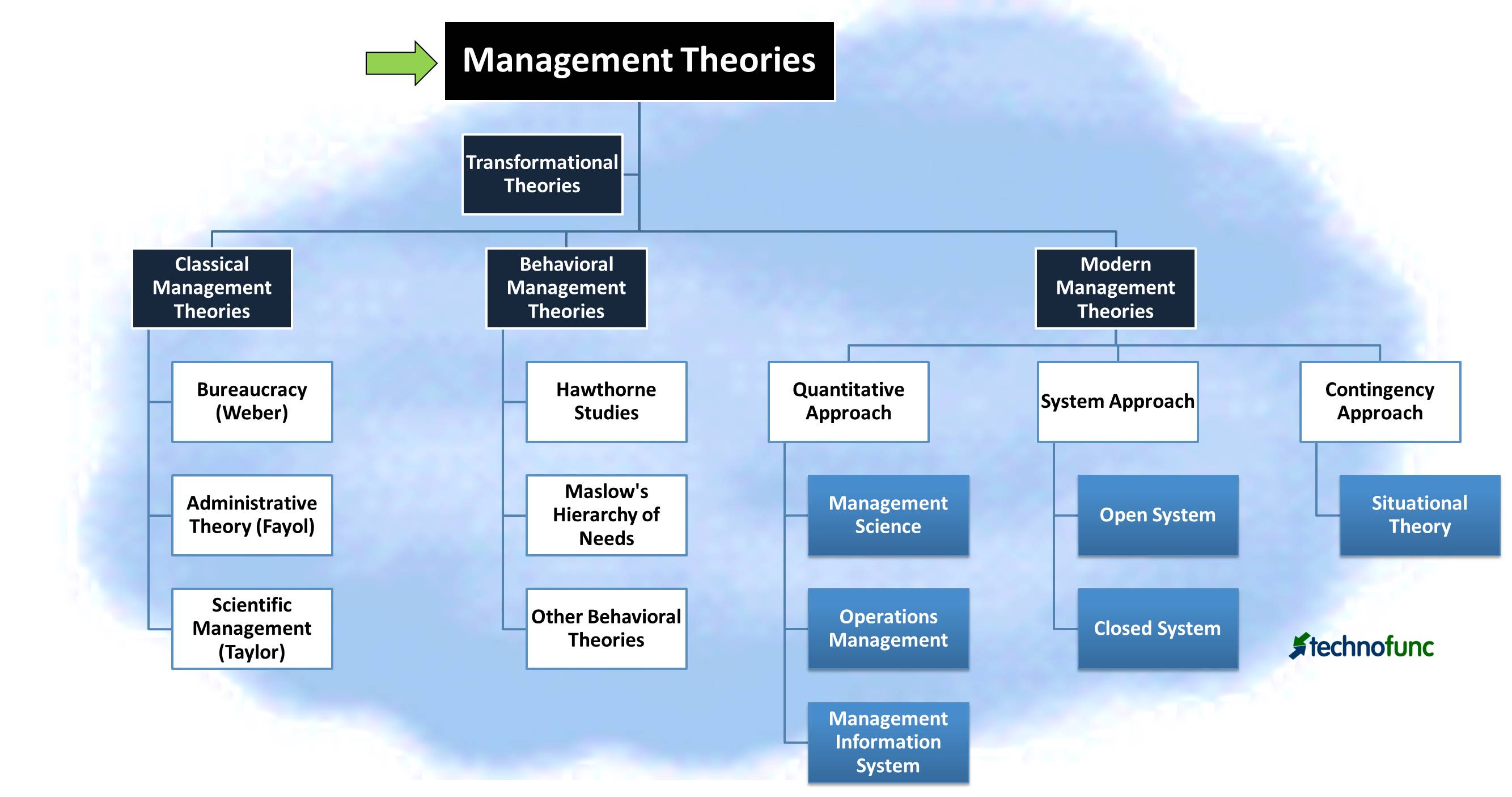
Types of Management Theories
Management theories can be classified into three types.
- Classical Management Theory
- Behavioral Management Theory
- Modern Management Theory
These management theories are explained below:
1. Classical Management Theory
Classical management theory is based on the belief that workers only have physical and economic needs and prescribes specialization of labor. Classical theories recommend centralized leadership and decision-making and focus on profit maximization. Three streams of classical management theory are - Bureaucracy (Weber), Administrative Theory (Fayol), and Scientific Management (Taylor).
2. Behavioral Management Theory
The behavioral management theory is focused on the human aspects of work. They are also often referred to as the human relations movement. These theories aspire to gain a better understanding of human behavior at work to improve productivity. It focuses on behavioral aspects like motivation, conflict, expectations, and group dynamics.
3. Modern Management Theory
Modern management theory emphasizes the use of systematic mathematical techniques to analyze and understand the inter-relationship of management and workers in all aspects. Three streams of modern management theories are - Quantitative Approach, System Approach, and Contingency Approach.

General Management Theories
There are four general management theories.
- Frederick Taylor – Theory of Scientific Management
- Henri Fayol – Administrative Management Theory
- Max Weber - Bureaucratic Theory of Management
- Elton Mayo – Behavioral Theory of Management (Hawthorne Effect)
1. Frederick Taylor’s Theory of Scientific Management:
Taylor’s theory of scientific management aimed at, improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. Taylor had a simple view about, what motivated people at work, - money. He felt that workers should get a fair day's pay for a fair day's work, and that pay should be linked to the amount produced. Therefore he introduced the differential piece rate system, of paying wages to the workers.
Taylor's Differential Piece Rate Plan:
- If Efficiency is greater than the defined Standard then workers should be paid 120 % of the Normal Piece Rate.
- If Efficiency is less than standard then workers should be paid 80% of the Normal Piece Rate.
Principles of Scientific Management
Four Principles of Scientific Management are:
- Time and motion study: - Study the way jobs are performed and find new ways to do them.
- Teach, train, and develop the workman with improved methods of doing work. Codify the new methods into rules.
- The interest of the employer & employees should be fully harmonized so as to secure mutually understanding relations between them.
- Establish fair levels of performance and pay a premium for higher performance.
2. Henri Fayol’s Administrative Management Theory:
Henri Fayol known as the Father of Management laid down the 14 principles of Management. These 14 principles of management are used to manage an organization and are beneficial for prediction, planning, decision-making, organization and process management, control, and coordination.
- Division of Work: Improves productivity, efficiency, accuracy, and speed
- Equity: Employees should be treated equally and respectfully
- Discipline: Makes the management job easy and make progress
- Initiative: support and encourage employees taking initiatives
- Authority and Responsibility: Efficient delivery of work with defined responsibility
- Esprit de Corps: Develop trust and mutual understanding
- Subordination of Individual Interest: Company over personal interest and respect the chain of command
- Stability: offer job security to their employees
- Remuneration: motivating factor linked to the individual’s efforts
- Unity of Direction: Unified goals and motives for all personnel working in a company
- Centralization: Balance between the hierarchy and division of power
- Scalar Chain: Hierarchy steps should be from top to the lowest
- Unity of Command: More than one boss brings a conflict of interest and confusion
- Order: the positive atmosphere in the workplace boosts productivity
3. Max Weber’s Bureaucratic Theory of Management:
Weber made a distinction between authority and power. Weber believed that power educes obedience through force or the threat of force which induces individuals to adhere to regulations. According to Max Weber, there are three types of power in an organization:-
- Traditional Power
- Charismatic Power
- Bureaucratic Power or Legal Power.
Features of Bureaucracy:
- Division of Labor.
- Formal Hierarchical Structure.
- Selection based on Technical Expertise.
- Management by Rules.
- Written Documents.
- Only Legal Power is Important.
- Formal and Impersonal relations.
4. Elton Mayo’s Behavioral Theory of Management:
Elton Mayo's experiments showed an increase in worker productivity was produced by the psychological stimulus of being singled out, involved, and made to feel important. Hawthorne Effect can be summarized as “Employees will respond positively to any novel change in a work environment like better illumination, clean work stations, relocating workstations, etc. Employees are more productive because they know they are being studied.
5 Relationship Theories or Transformational Theories of Management
Relationship theories (also known as "Transformational theories") focus upon the connections formed between leaders and followers. These leaders motivate and inspire people by helping group members see the importance and utility of the task. Transformational leaders are focused on the performance of group members, but also want each person to fulfill his/her potential. These leaders often have high ethical and moral standards.
There are different thoughts on management. According to one school of thought, history is of no relevance to the real problems faced by modern world managers in today's dynamic environment. However, both management theory and its history are indispensable tools for managing complex digitally-enabled organizations in a modern context.
Forces Influencing Management Theories
The following three forces had a major influence on the concept and evolution of management theories.
Social Forces:
Social forces are the norms and values that characterize a culture. Early social forces allowed workers to be treated poorly. However, more recent social forces have provided for more acceptable working conditions for the workforce. Social forces have greatly influenced the management thought in the areas of motivation and leadership.
Economic Forces
Economic factors have influenced the way businesses developed and designed their organizational structures, workforce, etc. Examples of these economic forces are Ideas like a market economy, public enterprise, and private ownership of property, economic freedom, competitive markets, and globalization.
Political Forces
Political forces such as governmental regulations play a significant role in how organizations choose to manage themselves. Government actions and political realities often influence the success and failure of a business and most of the time political factors that affect a business are often completely out of the company's control. Political forces have influenced management theory in the areas of environmental analysis, planning, control, and organizational design and employee rights.
Suggested Reading and Resources
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Team Foundation in Forming Stage
This is the first stage of team development. This is the stage when the foundation of the team is laid. During the Forming stage, team members have a high dependence on their leader for guidance. Learn the practical strategies you can use during this stage to help your team develop into a highly effective performing team.
-
Process & Stages of Creativity
Creative ideas do not come just like that. There is a process to it. There are a number of techniques of creativity to support the generation of ideas but the widely practiced ones are brainstorming and lateral thinking. Most innovations are not so much the product of sudden insights as they are the result of a conscious process that often goes through multiple stages. The creative process can be divided into four stages of preparation, incubation, evaluation, and implementation.
-
What are the functions which a leader does to establish as a leader? What are the activities undertaken by them to become great leaders, rather revolutionary leaders? The most important tasks done by a leader in all situations are defining the vision, mission, and goals, leading the team, administrative functions, motivating followers, decision making and conflict resolution, and continuous development.
-
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory that explains that people are motivated by five basic categories of human needs. These needs are physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. There is a little scientific basis for this concept of a hierarchy of needs.
-
The best career choices are ones that match your values. Each person has several values that are important to him. These values are highly personal and knowing them provides a clearer sense of what's most important to you in your life and career. Career values are the beliefs you consider important from a work standpoint. Values help you understand what you want from a job? Explore a few examples of work values that can influence career path and job satisfaction.
-
At different points in your professional career, it is helpful to identify your core values. Values are the qualities considered to be the most important guiding principles that determine the priorities in your life and greatly influence your career choices. Your career brings happiness when it is in agreement with the beliefs you have about what is important and meaningful to you. Awareness of your values will help you develop a clearer sense of what's most important to you in life.
-
Frederick Winslow Taylor started the “Scientific Management Movement”, and attempted to study the work process scientifically. Scientific management, also called Taylorism, was a theory of management that analyzed and synthesized workflows. It is a system for increasing the efficiency of manpower to its maximum potential and streamlining production to improve efficiency. This article explores this theory in more detail.
-
Thinking & Problem Solving Skills
Today's dynamic business world demands that you make decisions that significantly boost productivity and drive competitive advantage. But how do you know whether a decision will benefit the organization? And how do you know that the decisions are based on rational and statistical reasoning? Explore how to become a dynamic problem solver with the skills to make accurate decisions.
-
Behavioral Approach to Management
The behavioral management theory had a profound influence on management by focusing on understanding the human dimensions of work. It is also called human relations movement as behavioral theorists focused on managing productivity by understanding factors of worker motivation like their needs and expectations, personality, attitudes, values, group behavior, conflict, and group dynamics. It advocated the use of psychological techniques to motivate employees.
-
Managers have to perform many roles in an organization, and how they handle various situations will depend on their style of management. Management styles are the characteristic ways, of making decisions relating to subordinates. These are the strategies, efforts, or direction used by the manager, to create an efficient workplace, to achieve organizational goals. A management style is the method of leadership used by a manager.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










