- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- Order to Cash
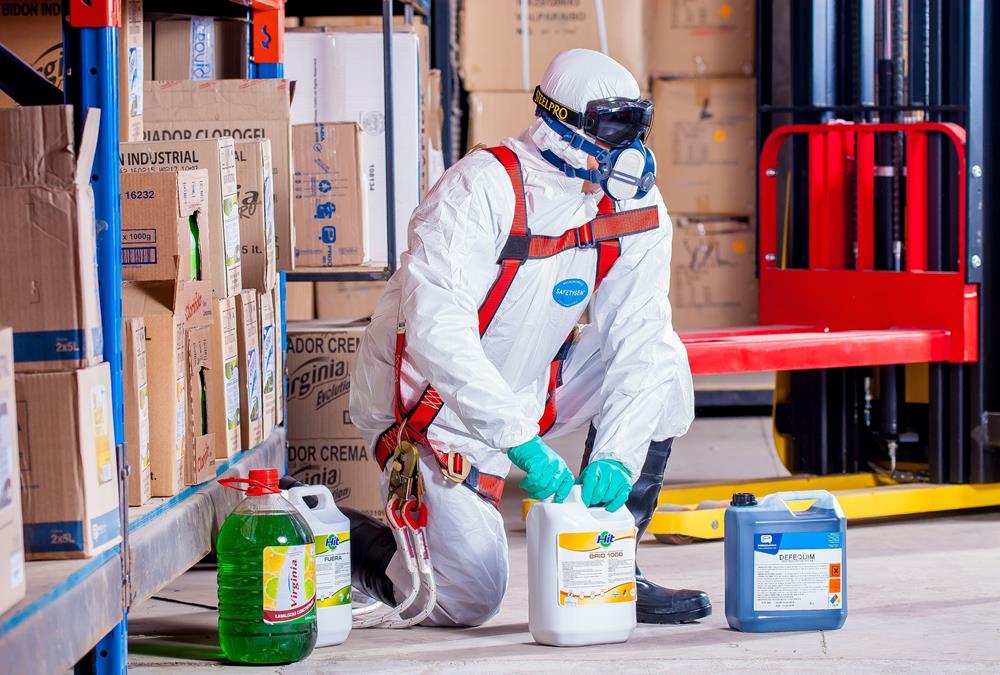
- Outbound Picking Process
Outbound Picking Process
When a customer wants a product that has been stored in the warehouse, the same need to be picked off the shelf (or off the floor) and get it ready for shipping. Depending on how big is the warehouse, picking can take a while. (Many distribution centers cover more than 1 million square feet.). Hence, warehouse order picking methods are an important aspect within any warehouse.
When a customer wants a product that has been stored in the warehouse, the same need to be picked off the shelf (or off the floor) and get it ready for shipping. Depending on how big is the warehouse, picking can take a while. (Many distribution centers cover more than 1 million square feet.). Hence, warehouse order picking methods are an important aspect within any warehouse. Compared to shipping, storage, and receiving stages, order picking forms as much as 55% of operation costs in a distribution center.
If two customers order the same product, one need to pick both items at the same time. And if a single customer orders two products, one would want to pick both products during the same trip. When you think about how much time it takes to travel between where items are stored and where they’re packaged for shipment, you see how
important defining an efficient picking process could be. It has a direct impact on how satisfied your customers are. If your picking methods in the warehouse are quick and accurate, your business will succeed.
This topic describes the picking process in detail and the variations used across industry to design this activity. We will also focus on some best practices deployed across industry. A warehouse management system should generate pick lists for each picker to retrieve items in the most efficient way. For each new order, the picker will receive a packing slip of the items ordered and storage locations at the warehouse. The picker will collect the ordered products from their respective locations. This may include zone picking, wave picking, or batch picking.
What Is Order Picking?
Order picking is the process of selecting items from a warehouse , to fulfill customer orders. When it comes to warehouse order picking methods, the choices you make have a big impact on your supply chain. Choosing the right order picking strategies will go a long way for your business, leading to improvements such as reduced labor costs, improved customer service, and the best use of warehouse space.
The Importance of Order Picking
The order picking process involves pulling items from inventory to fill a customer’s order. This is often seen as the most labor-intensive task within a warehouse. Since order picking often requires heavy physical labor, the process can be slow, affected by human error, and unproductive. Getting customers their orders on time is crucial to the success of any brand or business.
Use of Technology
Technologies introduced in the past few years are make picking more efficient. Given below are some recent innovations:
- A warehouse execution system uses sophisticated routing algorithms.
- Define pick paths that minimize time and distance.
- Use of robots for picking the orders.
- Pick-to-light systems and other displays to give pickers visual cues.
- Pick-to-voice systems telling pickers where to go and what to pick
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Warehouses can be places where piles of packed or loose products occupy space. If left disorganized, it will become very challenging to identify products for packing or picking. Hence, proper organization of warehouse is very important. Warehouse labeling systems eliminate this problem by making sure products are easily identified and managed during the warehousing and shipping process. Labeling is the most functional and cost-effective way to keep your warehouse organized and operating efficiently.
-
After products have been received and passed a quality inspection, they need to be stored so that you can find them when you need them. This process is called putaway. The spot where you store a particular product is called a location. One section of a warehouse might have small locations for light items; another area may have large locations on the floor for heavy items.
-
One of the most important decisions when running a warehouse is its layout. Warehouse layout defines the physical arrangement of storage racks, loading and unloading areas, equipment and other facility areas in the warehouse. A good layout aligned with the business needs could have a significant effect on the efficiency.
-
Warehouse management and distribution logistics involve the physical warehouse where products are stored, as well as the receipt and movement of goods takes place. Warehouse management aims to control the storage and movement of products and materials within a warehouse. These operations include the receipting of inwards goods, tracking, stacking and stock movement through the warehouse.
-
Warehouses may seem like a simple, straightforward concept, but they actually include a variety of different types of warehouses that all have their own niche. The type of warehousing that’s right for you depends on your specific industry, location, and needs. From private warehousing, distribution centers, and climate-controlled warehouses, there’s an option to suit every business.
-
What is the difference between Warehouse Management & Inventory Management?
The terms “inventory management” and “warehouse management” are sometimes mistakenly used interchangeably as they both deal with operations and products of industries. Despite their few similarities, there are many notable differences between warehouse and inventory management systems.
-
Transport operations are often divided into full load and part load and due to economies of scale, the unit costs are higher for part loads. Our customer needs several part loads delivering, so it can reduce costs by consolidating these into full loads. Then it gets all the part loads delivered to a warehouse near the suppliers, consolidates them into full loads, and pays the lower costs of full-load transport to its operations.
-
Overview of Third-Party Logistics
Third-party logistics (abbreviated as 3PL, or TPL) is an organization's use of third-party businesses to outsource elements of its distribution, warehousing, and fulfillment services. A third-party logistics provider (3PL) is an asset-based or non-asset based company that manages one or more logistics processes or operations (typically, transportation or warehousing) for another company.
-
Business Case of Multiple Warehouses
Adding extra warehouses to business provides many benefits such as reducing shipping costs, increasing storage capacity, and having warehouses for specific purposes to simplify overall warehouse management. Multiple warehouses allow you to organize your inventory in a way that helps your business be more effective.
-
When products arrive at a facility, there need to be a defined process to let them in. The process for accepting inventory when it arrives is called "Receiving". Any warehousing operation must be able to receive inventory or freight from trucks at loading docks and then stow them away in a storage location. Receiving often involves scheduling appointments for deliveries to occur, along with unloading the goods and performing a quality inspection.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved