- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- Cash Management
- Cash Management - Integrations
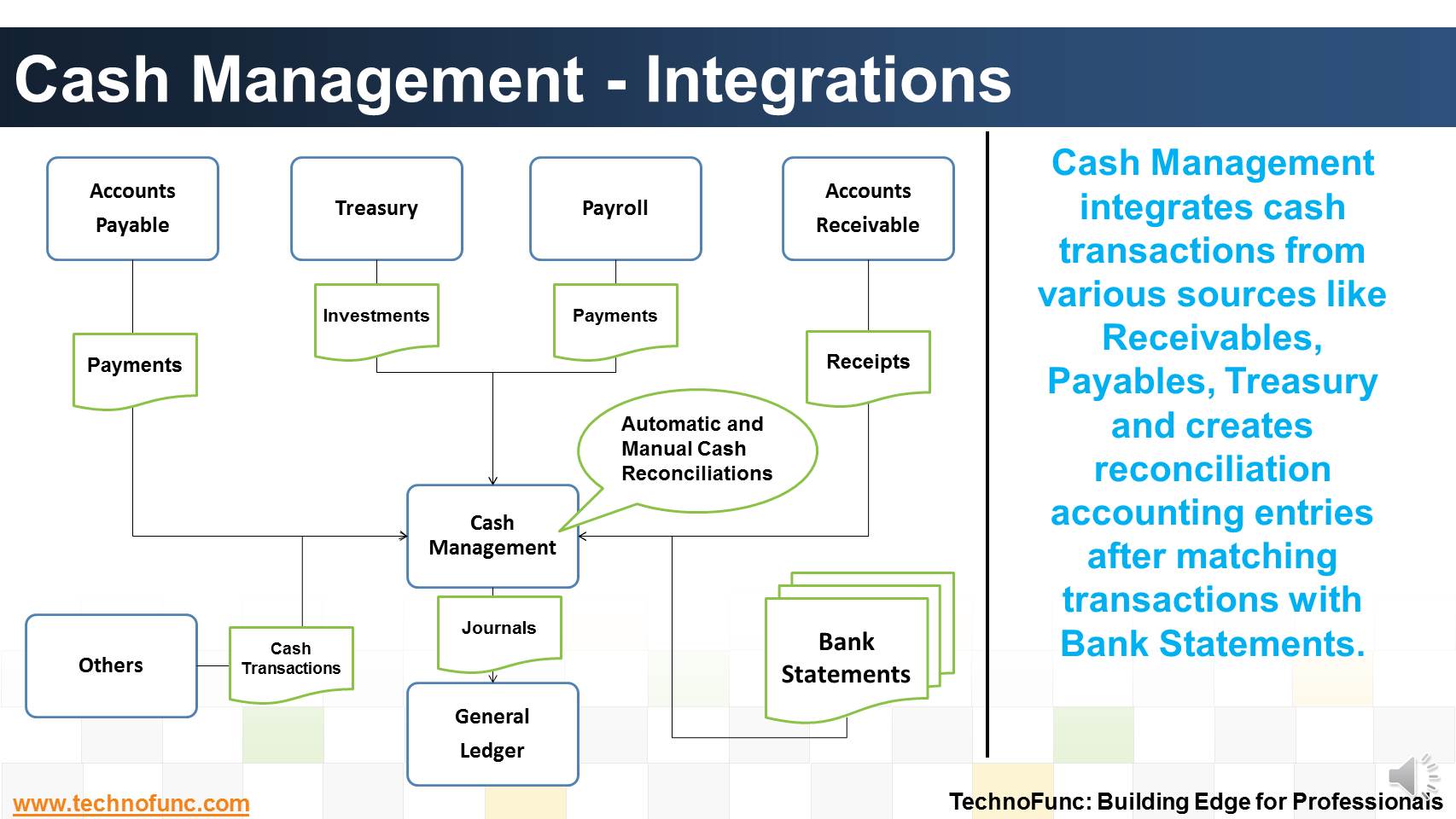
Cash Management - Integrations
Cash Management integrates cash transactions from various sources like Receivables, Payables, Treasury and creates reconciliation accounting entries after matching transactions with Bank Statements.
Cash Management receives payment information from Accounts Payables and you can then clear and reconcile payments. You can also create miscellaneous non-invoiced transactions, such as bank charges, debits, or credits.
Similarly, Cash management gets receipt information from Accounts Receivables. Using Cash Management, you can clear and reconcile receipts and create miscellaneous (non-invoiced) transactions, such as interest, debits, or credits.
Similarly, Cash management gets investment and deal information from Treasury. Using Cash Management, you can clear and reconcile investments.
You can get cash transactions from other sources like payroll or intercompany system.
Transactions are cleared and reconciled against a bank statement; reconciliation accounting entries are created after matching transactions and sent to General Ledger.
One of the most recurring theme in global transaction banking is the increasing integration of cash management and trade finance products.
This is possible only if the organization has a well defined Centralized Treasury Management System. This brings tangible benefits to both corporates and financial institutions.
To Learn more about how treasury and cash management integration can benefit organizations, please see our video on Treasury Management Process.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Treasury Management - Benefits
Effectively using treasury management with cash management and trade finance products brings tangible benefits to both corporates and financial institutions. Let us discuss some tangible benefits of treasury function.
-
Account Reconciliation – How? Learn the three key attributes to perfom account reconciliation.
-
The Cash Management component ensures that the enterprise has sufficient liquidity for payments that are due and to monitor payment flows. Learn how treasury plays an important role in cash management for the enterprise.
-
How the inflow and outflow of cash is linked to the operating cycles of the business? Learn the cash management process in an enterprize and it's key components.
-
What are the various sources of cash in an organization. Which sources increase the cash available with the enterprise and which sources results in outflow of the cash? Let us explore!
-
Effectively using cash management with trade finance products brings tangible benefits to both corporates and financial institutions.Learn the various benefits of cash management process.
-
In manual clearing, Bank statement details are to be matched manually considering certain rules. Learn the steps involved in manual clearing of bank transactions.
-
Unravel the mystery behind clearing. Why we use clearing accounts. Find the relevance of word "Clearing" in business context.
-
What is Invoice to Cash Process
In this article, we will explore the business process area known as; Invoice to Cash; Also known as I2C. Learning objectives for this lesson are: Meaning of Invoice to Cash Process; Sub Processes under Invoice to Cash; Process Flow for Invoice to Cash; Key Transactions Fields; Key Setups/Master Data Requirements.
-
Before we dive into cash management, let us fist understand what we mean by cash and what constitutes cash in context of cash management process.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved











