- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- Cash Management
- Bank Statement Lines
Bank Statement Lines
So many codes in the lines that are there in a Bank Statement. It contain lots and lots of meaningful information that can help automated many tasks. Explore more!
Bank Statement Lines
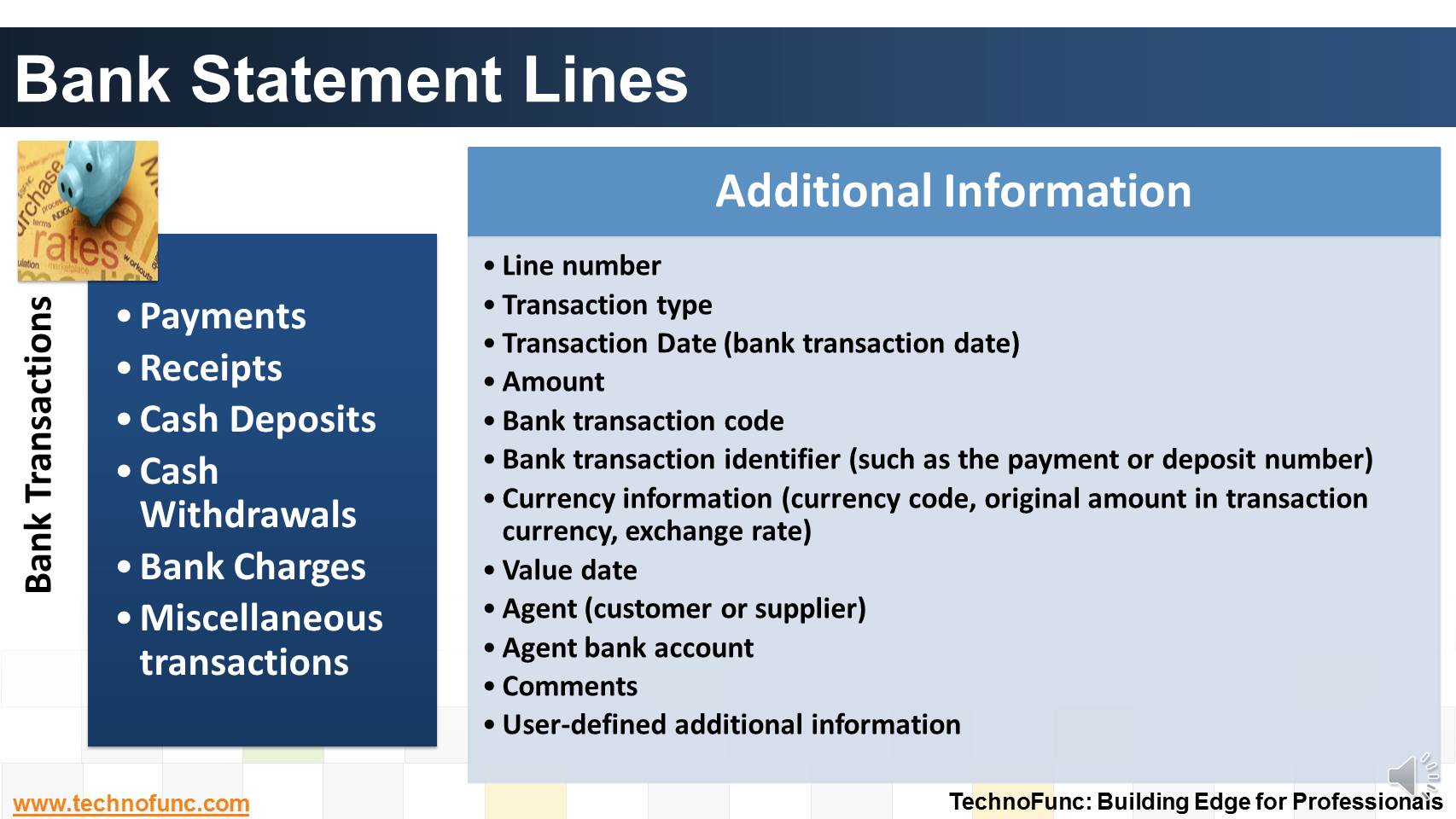
Given below are the types of transactions that generally constitute a bank statement-
- Payments
- Receipts
- Cashflows
- Miscellaneous transactions
- Each transaction is further supported with additional information.
The typically available information is could be of the nature shown here.
This additional information is very critical for automated reconciliations as you will notice in the upcoming articles.
Additional Information
- Line number
- Transaction type
- Transaction Date (bank transaction date)
- Amount
- Bank transaction code
- Bank transaction identifier (such as the payment or deposit number)
- Currency information (currency code, original amount in transaction currency, exchange rate)
- Value date
- Agent (customer or supplier)
- Agent bank account
- Comments
- User-defined additional information
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Treasury Management - Functions
Treasury management has become an specialized function. Treasury function helps in managing the Risk-return profile as well as the tax-efficiency of investment instruments. In larger firms, it may also include trading in bonds, currencies and financial derivatives. Learn about the various tasks, activities and imperatives, undertaken by treasuries in in today's context.
-
Technology has enabled the treasury function by providing various solutions to manage it's complicated tasks. This article explains various types of treasury management systems available in the market.
-
The terms Treasury Management and Cash Management are sometimes used interchangeably, while, in fact, the scope of treasury management is larger and includes funding and investment activities as well. Learn all about Treasury Management here!
-
What is Invoice to Cash Process
In this article, we will explore the business process area known as; Invoice to Cash; Also known as I2C. Learning objectives for this lesson are: Meaning of Invoice to Cash Process; Sub Processes under Invoice to Cash; Process Flow for Invoice to Cash; Key Transactions Fields; Key Setups/Master Data Requirements.
-
In the previous article we talked about the meaning of the account reconciliations. Now as you now the definition of account reconciliation, in this article let us see why it is carried out.
-
Cash Clearing – Accounting Entries
The Cash Clearing process enables you to track amounts that have actually cleared your bank. Learn the steps and accounting entries that gets generated during the cash clearing process.
-
Treasury has increasingly become a strategic business partner across all areas of the business, adding value to the operating divisions of the company. Managing activities that were traditionally carried out within the general finance function. Learn about the drivers for this change.
-
Suspense and clearing accounts resemble each other in many respects but there exists important fundamental difference between the two. Read more to explore these differences.
-
So many codes in the lines that are there in a Bank Statement. It contain lots and lots of meaningful information that can help automated many tasks. Explore more!
-
Collection Float is the time spent to collect receivables. Collection float is the sum total of time taken by Invoice Float; Mail Float; Processing Float and Availability Float. Explore more!
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved











