- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- Procure to Pay
- What is a Warehouse & why companies need them?
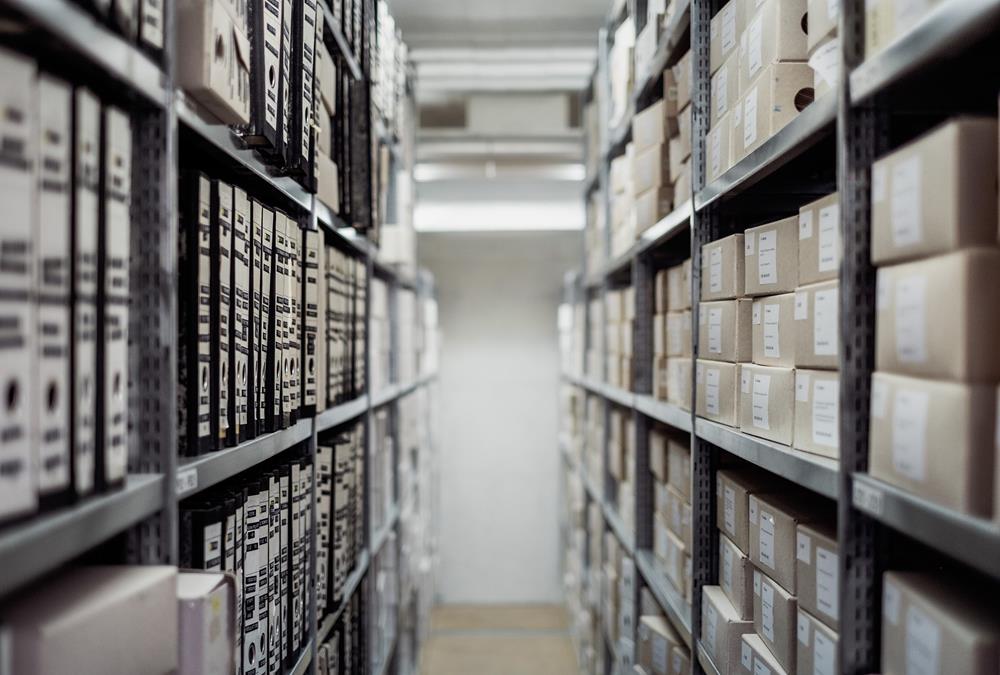
What is a Warehouse & why companies need them?
All organizations hold stocks. In virtually every supply chain, gaps exist between when something is produced and when a customer is ready to buy or receive it. Stocks occur at any point in the supply chain where the flow of materials is interrupted. This implies that products need to be stored during this period of gap.
All organizations hold stocks. In virtually every supply chain, gaps exist between when something is produced and when a customer is ready to buy or receive it. Stocks occur at any point in the supply chain where the flow of materials is interrupted. This implies that products need to be stored during this period of gap. Simply put, warehouse is a building for storing goods. Most organizations arrange for stocks to be kept in warehouses. A warehouse is any location where stocks of material are held on their journey through supply chains.
Other than providing storage, warehouses also fulfill a range of commercial functions like receiving the goods, stockpiling and dispatching goods to customers; during the process also displaying goods for commercial buyers; packing, checking and labelling orders, and dispatching them.
Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc.
They usually have loading docks to load and unload goods from trucks. Sometimes warehouses are designed for the loading and unloading of goods directly from railways, airports, or seaports. They often have cranes and forklifts for moving goods, which are usually placed on standard pallets loaded into pallet racks. Apart from storage, they are used to inspect, sort materials and break bulk (taking large deliveries and breaking them into smaller quantities). They might also be used for finishing products, labelling, packaging, making products ‘store ready’ for retailers, doing other aspects of postponement, servicing vendor managed inventories, and so on.
Why we need Warehousing?
Once the goods have been manufactured, someone owns the products till they are delivered to end customers and has its money tied up in them. Hence someone needs to keep track of where those products are and protect them from damage. Warehouse enables the businesses to stockpile these goods and manage them before further distribution. Storage also includes a proper arrangement for maintaining goods from the time of their manufacturing or purchase till they are truly used. When storage is managed on a large scale and in a particular manner it is known as warehousing. Warehousing is one of the essential elements in current day business without which business is not possible.
Given below are the key benefits of the warehouse:
- Safety and Preservation of goods, preventing them from getting lost or stolen.
- Trouble free handling, reduce errors and damages in the order fulfillment process.
- Ensuring Continuous supply of products, ensuring timely delivery and optimized distribution.
- Warehouses helps price stabilization by creating time utility.
- Serve as local and regional store distribution centers and provide the facilities of packing, processing and grading of goods.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Business Case of Multiple Warehouses
Adding extra warehouses to business provides many benefits such as reducing shipping costs, increasing storage capacity, and having warehouses for specific purposes to simplify overall warehouse management. Multiple warehouses allow you to organize your inventory in a way that helps your business be more effective.
-
Before shipping, businesses need to make sure that the items will arrive in good condition. Packaging is a form of protection against environmental threats that the product will face from the time it leaves warehouse facility until the time it reached the customer. The packaging is intended to provide protection for the item as it is being handled in the warehouse or when the item is being shipped.
-
At a high level, the essential elements in a warehouse are an arrival bay, a storage area, a departure bay, a material handling system and an information management system. As part of the process for enabling a warehouse layout, you must define warehouse zone groups, and zones, location types, and locations.
-
After products have been received and passed a quality inspection, they need to be stored so that you can find them when you need them. This process is called putaway. The spot where you store a particular product is called a location. One section of a warehouse might have small locations for light items; another area may have large locations on the floor for heavy items.
-
Warehouses may seem like a simple, straightforward concept, but they actually include a variety of different types of warehouses that all have their own niche. The type of warehousing that’s right for you depends on your specific industry, location, and needs. From private warehousing, distribution centers, and climate-controlled warehouses, there’s an option to suit every business.
-
Resource Planning is the process of planning for expected workload and determining the number of resources required to complete each activity in the warehouse. There are many types of warehouse positions, and they also vary by the employer, the scale of operations and location. Discussed here are generic positions applicable to warehouse management processes.
-
To stay competitive in today’s tough market, the location of your warehouse is vital. To grow retail business need to offer to customers faster and affordable shipping time, which is dependent on the warehousing location as the location of the warehouse affects the transit time to ship orders to customers.
-
When products arrive at a facility, there need to be a defined process to let them in. The process for accepting inventory when it arrives is called "Receiving". Any warehousing operation must be able to receive inventory or freight from trucks at loading docks and then stow them away in a storage location. Receiving often involves scheduling appointments for deliveries to occur, along with unloading the goods and performing a quality inspection.
-
Miscellaneous Warehouse Processes
At the end of each inventory control, the Contractor provides the Ordering Person with an inventory report which contains a list of all stock adjustments. The Ordering Person uses the report to create, by use of his/her own means, necessary value and accounting adjustments related to the stock. Let us look at some to the mislaneous warehouse processes not covered earlier.
-
What is the difference between Warehouse Management & Inventory Management?
The terms “inventory management” and “warehouse management” are sometimes mistakenly used interchangeably as they both deal with operations and products of industries. Despite their few similarities, there are many notable differences between warehouse and inventory management systems.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved