- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Journal Entry & Import
GL - Journal Entry & Import
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
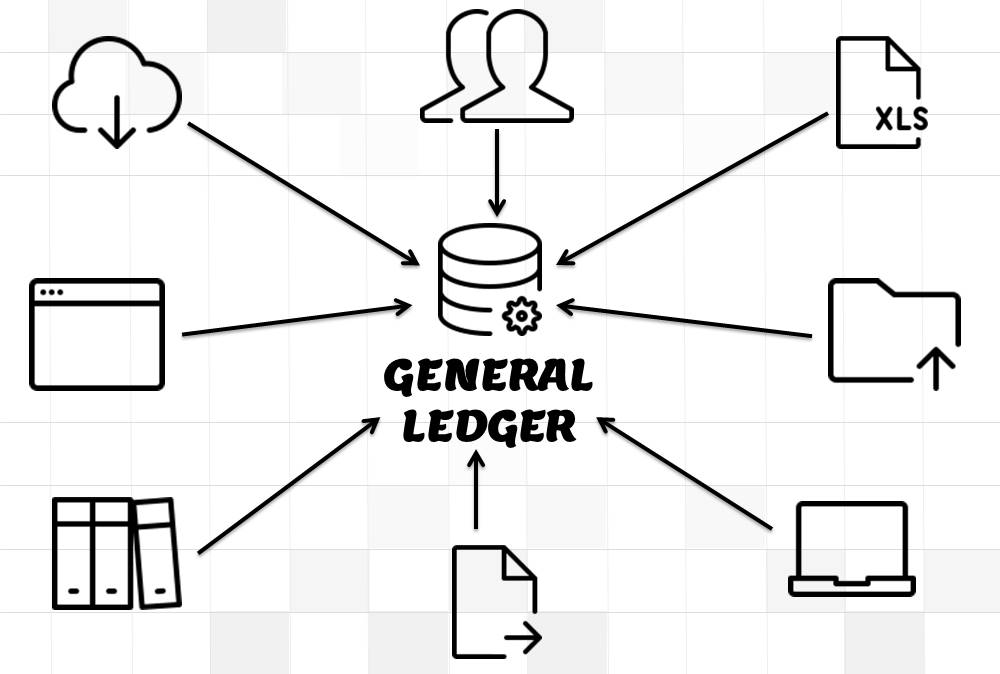
Recording Journals in General Ledger:
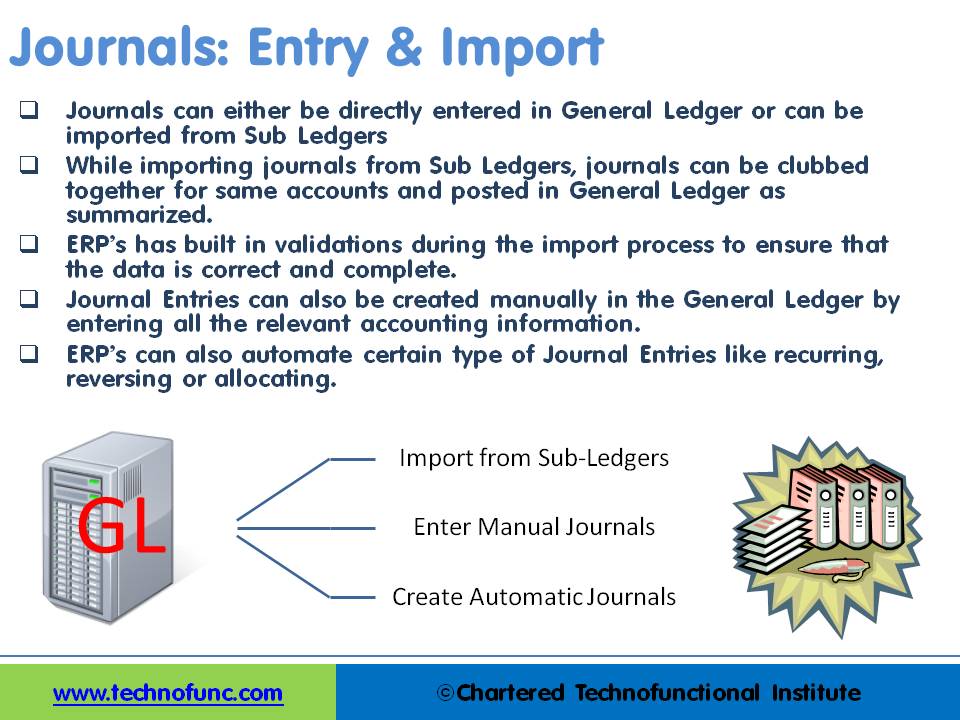
Journals can either be directly entered in General Ledger or can be imported from Sub Ledgers. Most of the journals are created along-with business transactions like sales, purchases, receipts, and payments and get recorded in respective sub-ledgers. As sub-ledgers generally capture data at a more granular level, the relevant accounting information must flow to the general ledger for posting and subsequent reporting. From sub-ledgers, they need to be imported to the general ledger for financial recording and reporting.
Journal Entries can also be created manually in General Ledger by entering all the relevant accounting information. ERPs can also automate certain types of Journal Entries like recurring, reversing, or allocating journals. In case of manual entry follow the steps and guidelines outlined in the Recording Journals tutorial.
Importing – Detail V/s Summarized:
While importing journals from Sub Ledgers, journals can be clubbed together for the same accounts and posted in General Ledger as summarized.
Various general ledger systems provide the functionality to create Summary Journals which summarize all transactions for the same account, period, and currency into one debit or credit journal line. This results in fewer transactions in the general ledger systems and makes financial reports more manageable in size. In the case of summary journal users, lose the one-to-one mapping of detail transactions in the sub-ledger to the summary journal lines created by the import process. However most of the organizations use this feature as this prevents too many transactions in GL Accounts and transactions get clubbed based on category, type, or transaction source.
Using the drill-down functionalities available in most of the modern general ledger systems, users can still perform various review and analysis functions, as even if the system creates summary journals, it can still maintain a mapping of how Journal Import summarizes sub-ledger detail transactions from feeder systems into general ledger journal lines.
Journal Import Validations:
ERP’s and automated accounting systems must have built in validations during the import process to ensure that the data is correct and complete. An effective Journal Import program should validate key accounting information before it creates journal entries in the General Ledger application to prevent errors and reconciliation efforts.
Given below are some of the common data validations that can happen during the GL Import process:
1. Suspense Posting:
Suspense posting puts the remaining amount in the suspense account in case the debits and credits of the journal are not matching. In case it is not required, Journal Import should reject all invalid lines that do not balance.
2. Duplicate Batch Name:
If the batch name is a unique field then Journal Import should ensure that a batch with the same name does not already exist for the same period in the General Ledger application. Similarly, it must also check to ensure that more than one journal entry with the same name does not exist for a batch.
3. Other Attributes:
Attributes that can be validated to ensure that journals contain the appropriate accounting data could be accounting books, period, source, currency, category, accounting date, reversal period, account validation, account code combinations, effective date, roll date, and any other required validations.
Import Using Excel:
In today’s accounting world, financial and operational data typically is stored in a variety of programs and formats. Excel is one of such tools, most widely used by the accountants! When accountants need to prepare a report based on data from various systems, the first step is to export the data into Excel. Many times accounting information is stored in chronological order in excels by the accountants, and examples include adjusting entries and recurring entries.
Benefits of using the excel upload feature are that it makes life much easier for data operator and accounts executives. The great flexibility of excel based application increases productivity and results in reduced training costs as most users are already familiar with the excel functionalities and also improves user acceptance for automated systems. The biggest benefit comes from the fact that excel upload can also work in disconnected environments.
Typically, most of the automated systems provide the functionality to import accounting data from Excel to the general ledger and create journals. Most ERPs provide the ability to upload journals using the MS Excel worksheet. You can create journals in Excel Template and upload directly to General Ledger.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
-
The general ledger is the central repository of all accounting information in an automated accounting world. Summarized data from various sub-ledgers are posted to GL that eventually helps in the creation of financial reports. Read more to understand the role and benefits of an effective general ledger system in automated accounting systems and ERPs.
-
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
-
Accrued expenses, sometimes referred to as accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts. Discuss the need to record accrued liabilities and why they require an adjustment entry. Understand the treatment for these entries once the accounting period is closed and learn to differentiate when the commitments become liabilities.
-
Global Business Services (GBS) Model
Global business services (GBS) is an integrated, scalable, and mature version of the shared services model. Global Business Services Model is a result of shared services maturing and evolving on a global scale. It is represented by the growth and maturity of the Shared services to better service the global corporations they support.
-
Period End Accruals, Receipt Accruals, Paid Time-Off Accruals, AP Accruals, Revenue Based Cost Accruals, Perpetual Accruals, Inventory Accruals, Accruals Write Off, PO Receipt Accrual, Cost Accrual, etc. are some of the most complex and generally misconstrued terms in the context of general ledger accounting. In this article, we will explore what is the concept of accrual and how it impacts general ledger accounting.
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
-
Record to report (R2R) is a finance and accounting management process that involves collecting, processing, analyzing, validating, organizing, and finally reporting accurate financial data. R2R process provides strategic, financial, and operational feedback on the performance of the organization to inform management and external stakeholders. R2R process also covers the steps involved in preparing and reporting on the overall accounts.
-
GL - Understanding Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by a business entity to record and categorize financial transactions. COA has transitioned from the legacy accounts, capturing just the natural account, to modern-day multidimensional COA structures capturing all accounting dimensions pertaining to underlying data enabling a granular level of reporting. Learn more about the role of COA in modern accounting systems.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved