- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Account Allocations
GL - Account Allocations
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
What is Account Allocation?
Allocation is the act of distributing according to a plan. As per the dictionary allocate means to set apart for a special purpose; designate; distribute according to a plan. From an accounting context, it means a system of dividing overhead expenses between the various departments of a business. Figuratively, earmarked is often used in regard to monetary allocations although it is heard in other contexts as well.
The allocation also refers to a piece of the pie, a share in the profits, a portion of whatever is being divided up and parceled out usually money, but in an accounting context is applicable to account balances. This expression probably has its origin in the graphic representation of budget allotments in circular, pie-shaped form, with various sized wedges or pieces indicating the relative size of allocations to different agencies, departments, etc.
Concept of Mass Allocations:
Mass allocations is a functionality offered by many automated systems and ERPs to distribute the account balances from one account to several others based on a formula or mathematic logic. Users can define a Mass Allocation formula to create journals that allocate revenues and expenses across a group of cost centers, departments, divisions, locations, and so on using any accounting dimension available. Users can include parent values in allocation formulas that can enable allocating to the child values referenced by the parent without having to enumerate each child separately.
Different Type of Allocations:
The commonly used allocations can be grouped as follows:
- Net Allocations: allocated amounts that reflect changes to the cost pool.
- Step–Down Allocations: distributing amounts from one allocation pool to a subsidiary allocation pool.
- Rate-Based Allocations: using current, historical, or estimated rates to allocate costs.
- Usage-Based Allocations: using statistics such as headcount, units sold, square footage, number of deliveries, or computer time consumed to calculate allocation amounts.
- Standard Costing Allocations: using statistics such as sales units, production units, number of deliveries or customers served to perform standard costing.
Examples of Allocation:
Allocations can be used in various practical business situations. For example, consolidated rent paid can be allocated to another division based on the area of usage, or, a pool of marketing costs can be allocated to several departments based on the ratio of department revenues to total revenues. Some of the commonly used examples are:
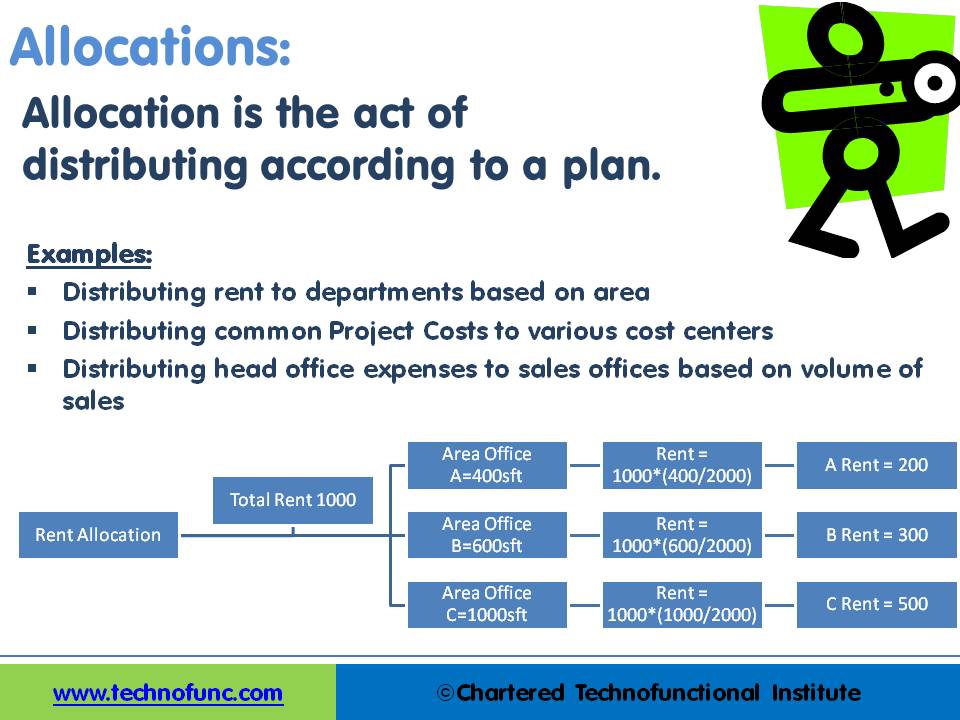
- Distributing rent to departments based on area
- Distributing common project costs to various cost centers
- Distributing head office expenses to sales offices based on the volume of sales
- Distributing marketing costs to product lines based on revenue
- Distributing common employee expenses to employee cost for assessments
In the example shown in the figure, we have a company which has taken a 1000 square feet office space on rent. The expenses for rent are borne by the head-office and payment to the landlord is also made by the head office. To know the true profitability of each of the departments (Department A, B & C) the rent needs to be allocated to each one of them.
Each department occupies different areas and the company has taken the measurement of the areas occupied by each of the departments. In the example shown here, the rent is being allocated to different departments based on their usage factor. This is an example of the concept of allocation and automated accounting systems help handle complex allocations programmatically.
Difference between Allocations & Recurring Journals:
Recurring Journals are for transactions that repeat every accounting period and allocation Journals are for single journal entry using an accounting or mathematical formula to allocate revenues and expenses across a group of accounting dimensions like cost centers, departments, divisions, locations, or product lines depending upon usage factors.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
-
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
-
In this article we will discuss various types of "Management Entities". Various types of operational units, are created by management, to effectively run, manage and control their business. Different types of functional units, and divisional units, are widely used across industry.
-
Period End Accruals, Receipt Accruals, Paid Time-Off Accruals, AP Accruals, Revenue Based Cost Accruals, Perpetual Accruals, Inventory Accruals, Accruals Write Off, PO Receipt Accrual, Cost Accrual, etc. are some of the most complex and generally misconstrued terms in the context of general ledger accounting. In this article, we will explore what is the concept of accrual and how it impacts general ledger accounting.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
Trial Balance in General Ledger
One of the greatest benefits of using a double-entry accounting system is the capability to generate a trial balance. What do we mean by trial balance? As the name suggests a trial balance is a report that must have its debits equals to credits. Understand the importance of trial balance and why it is balanced. Learn how it is prepared and in which format.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved