- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership Skills
- Leadership Theories
- Attribution Theory of Leadership
Attribution Theory of Leadership
The attribution theory of leadership deals with the formation of individual opinions about the reasons for particular events or observations. People will always try to understand why people do what they do. The leader will make a judgment about his employees based on his attribution of the causes of the employees' performance. Individuals will also make inferences about the leader and react to poor performance by the leader.
Attribution theory is attributed to the work done by Heider (1958), Jones and Davis (1965), and Kelley (1967, 1972, 1973). Attribution became an active area of organizational behavior research in the 1980s. It is a model of leadership evaluation that assumes that individuals make inferences about leadership ability by observing and interpreting certain environmental and behavioral cues. Attribution theory is best understood through an example. If you relate well with someone, you’re more likely to evaluate that person’s performance favorably; however on the other side, if someone else constantly irritates you the wrong way, you may be more inclined to evaluate that person’s performance punitively.
Attribution Theory:
People try to identify the reasons for observed events by collecting information that can help explain them. People constantly try to form chains of cause and effect explanations for observed incidents and experiences. These attributions by humans help them to assign an order to the world around them and increase their ability to understand the behavior of self and others.
Attribution Theory deals with the:
- Formation of individual opinions about the reasons for particular events or observations.
- Formation of opinions about the behavior of other people
- Formation of opinions about oneself
- How individuals explain their own successes and failures
- How individuals explain the behaviors and outcomes of others
- Whether the cause of the behavior is a characteristic of the follower (an internal attribute)
- Whether the cause of the behavior is a characteristic of the situation (an external attribute)
- Whether a follower's behavior is likely to remain constant (stable)
- Whether a follower's behavior is likely to change over time (unstable)
Attribution theory describes how individuals develop causal explanations for behaviors and outcomes, and how their causal explanations influence subsequent reactions. People see behavior as being caused either by the individual (i.e. dispositional) or by the environment (situational). It makes a distinction between internal and external causes.
Attribution Theory of Leadership:
It is a model of leadership evaluation that assumes that individuals make inferences about leadership ability by observing and interpreting certain environmental and behavioral cues. A two-step attributional model of leadership was proposed by Green and Mitchell (1979) suggesting that leaders make attributions (try to understand) about the cause of the performance before deciding on the appropriate action to take. A leader attributes various factor(s) for a follower's performance (internal, external, stable, unstable). These ascribed attributions influence leader's expectations for future performance as well as his behavior toward the follower.
The attribution model suggests that leaders observe their followers’ behavior, make inferences about the causes of that behavior (i.e., whether it is the result of internal, personal factors or of external, circumstantial ones), and then respond on the basis of those inferences. Attribution is the name given to this subjective process, in that we attribute causes, results, problems, and so on, to others, often with less than adequate information on which to base our judgment.
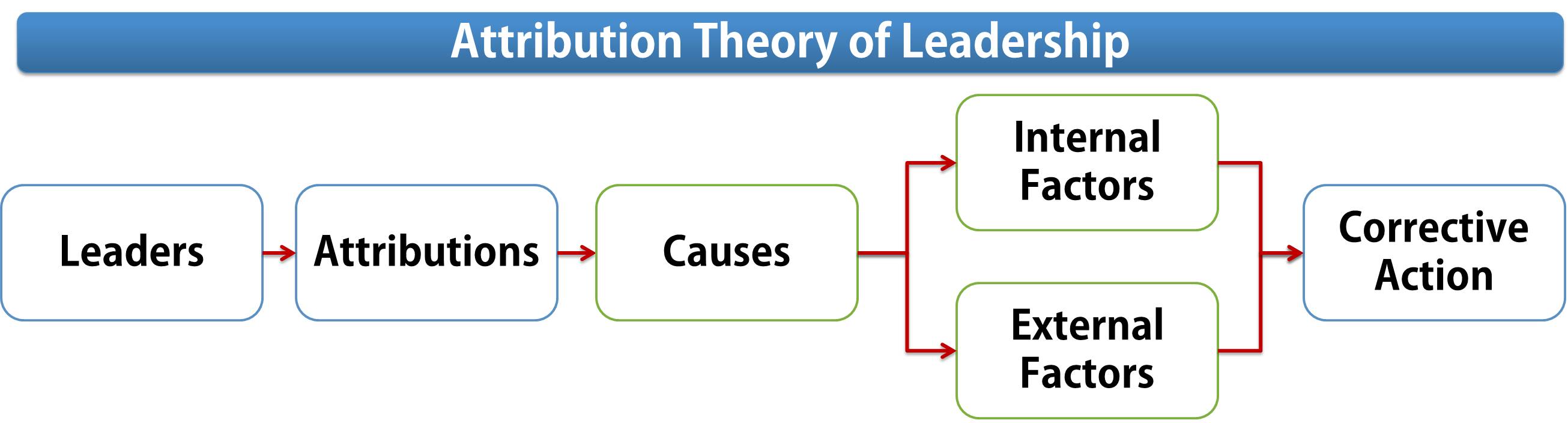
Internal Factors Influencing Behavior
Internal attributions include follower’s lack of interest, inexperienced followers, absenteeism by followers, or any other cause due to follower’s side.
If a leader attributes a follower's poor performance to internal factors such as low effort or a lack of ability, he or she may reprimand, dismiss, or provide training for the employee concerned. If a manager attributes an employee's poor performance to a lack of effort, then it will impact employees' performance appraisal poorly.
External Factors Influencing Behavior
External causes include, poor performance mainly due to machines break down, tool break down, material inventory problem, material quality problem, or any other cause by external factors, which are beyond the control of followers
If, however, poor performance is attributed to external factors such as a lack of material, or to work overload, the leader would need to concentrate on these factors and improve the situation instead of giving negative feedback to the employee. If a manager perceives that an employee's poor performance is due to a lack of skill, the manager may most likely assign the employee to required training or provide some assistance in terms of instructions or coaching.
Corrective Action by Leader
The leader will take corrective action:
- Towards the situation, if he attributes performance problems to external causal factors
- Towards follower when he attributes the performance problem to internal factors
For example, a manager who makes an internal attribution by concluding that an employee’s poor performance on a recent project was due to personal characteristics that led to lack of motivation, he is likely to decide on a harsher disciplinary action. Corrective action is more likely to be punitive in nature when attributed to lack of effort
However if he made an external attribution by assigning the reason of poor performance to the situation like a lockout situation say due to corona pandemic, the person was not able to visit clients and hence the decline in sales volume, the corrective action by the manager will be targeted towards remedying the situation.
Applicability to Organizations/Leadership
Attributions are critical to management because managers' and employees' judgments and actions are often based on perceived causes of behavior. Given below are some implications for organizations:
- Influence perception about employees based on observed performance and derived attributions to causes
- Managers will make a performance-related judgment based on observed behavior and attributions
- Inaccurate judgment about the causes of poor performance can have negative repercussions for the organization
- Attributions may influence employee motivation both positively and negatively
- Understanding attributions can improve managerial effectiveness
What is the attribution theory of leadership?
Attribution theory of leadership assumes that individuals make inferences about leadership ability by observing and interpreting certain environmental and behavioral cues. Leaders make attributions (try to understand) about the cause of the performance before deciding on the appropriate action to take. A leader attributes various factor(s) for a follower's performance (internal, external, stable, unstable). These ascribed attributions influence leader's expectations for future performance as well as his behavior toward the follower.
What is an example of attribution theory?
An example of attribution theory could be a manager who makes an internal attribution by concluding that an employee’s poor performance on a recent project was due to personal characteristics that led to a lack of motivation. Once he makes such a judgment, he is likely to decide on a harsher disciplinary action. In this case, the corrective action is more likely to be punitive in nature as it has been attributed by the manager to lack of effort.
What is an example of an external attribution?
An example of a manager making an external attribution is when he assumes that the poor performance of the employee is due to external situations. For example, due to lockdown situation created by corona pandemic, the employee was not able to visit clients to make sales calls, and hence there was an observed decline in sales volume. In this case, the manager has assigned the cause to external attribution and the corrective action by the manager will be targeted towards remedying the situation either by lowering his targets or looking for virtual sales opportunities.
What does the attribution theory mean?
Attributions theory means a lot for management because it establishes that managers' and employees' judgments and actions are often based on perceived causes of behavior. Managers make perceptions about employees based on observed performance and derived attributions to causes. Managers will eventually make a performance-related judgment based on observed behavior and attributions. These decisions based on attributions may influence employee motivation both positively and negatively and hence understanding attributions can improve managerial effectiveness.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Communication has as its central objective the transmission of meaning. The process of communication is successful only when the receiver understands an idea as the sender intended it. How does a message or an idea travel from one person to another? To transmit our message, we engage in a sensitive and complex process of communication, with different elements like sender, message, channels, receiver, noise, and feedback.
-
Servant Leadership is a recent revolutionary theory of leadership that focuses on leaders achieving authority rather than power. A servant leader considers the needs of others and tries to serve the followers by becoming a servant first. Servant leadership is leading with a desire to better serve others.
-
Robert Katz identified three leadership skills called - technical skills, human skills, and conceptual skills as the basic personal skills essential for leadership. Leaders must possess these three skills that assist them in optimizing a leader's performance. Technical skills are related to the field, human skills are related to communicating with people and conceptual skills related to setting the vision.
-
The skills approach to leadership suggests that certain skills are important for effective leadership. Skills are what leaders can learn and develop, whereas traits are innate characteristics. The main skills needed for leadership, according to one such theory, are technical, human, and conceptual.
-
Behavioral Theories of Leadership
Behavioral Theory of leadership is a big leap from Trait Theory, as it was developed scientifically by conducting behaviour focused studies. The theory emphasizes that leadership capability can be learned, rather than being inherent. This theory is based on the principle that a leader's behaviors can be conditioned in a manner that one can have a specific response to specific stimuli.
-
Normative leadership theories are built on moral principles and tell leaders how they ought to act. Victor Vroom formulated the normative model of leadership that specifically address leader behavior explicitly built on moral principles or norms. Normative leadership theories tell leaders how they should act to raise the moral performance inside the working group and manage their different responsibilities.
-
According to Environmental theories of leadership, a leader needs to deal effectively with environmental complexities and lead in a certain style as a result of environmental responses. Environmental influenced leadership demand leaders to learn how to adjust environmental factors. Leaders also have the responsibility of creating the right kind of environment for their followers by focusing on environmental factors and pressures.
-
In the field of communication studies, there are numerous models. No one model is suitable for all purposes and all levels of analysis. Some common models are known as Lasswell Model, George Gerbner Model, David Berlo Model, Shanon and Weaver Model, Osgoods Model, and Schramm Model. All these describe the four components of the communication process, namely, the source (communicator), the message, the channel, the receiver (audience).
-
Transactional Analysis also is known as the theory of human personality was proposed by Eric Berne in the 1950s. This theory of transactional leadership defines three different ego states in a person who engages in transactions with another person's ego states. These three ego states refer to major parts of an individual's personality and reflect an entire system of thought, feeling, and behavior.
-
Transformational Theories of Leadership
Transformational leadership theories focus on the leadership approach where the leader encourages, inspires employees to innovate and create positive and valuable organizational change. A transformational leader works towards “transforming” the culture to one that cultivates trust, mutual admiration, loyalty, and respect with the end goal of developing followers into leaders. Transformational leaders are known to be visionary, inspiring, daring, risk-takers, and thoughtful.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved